Figure 9. Neonatal androgen treatment blocks LH responses to ovariectomy in adulthood.
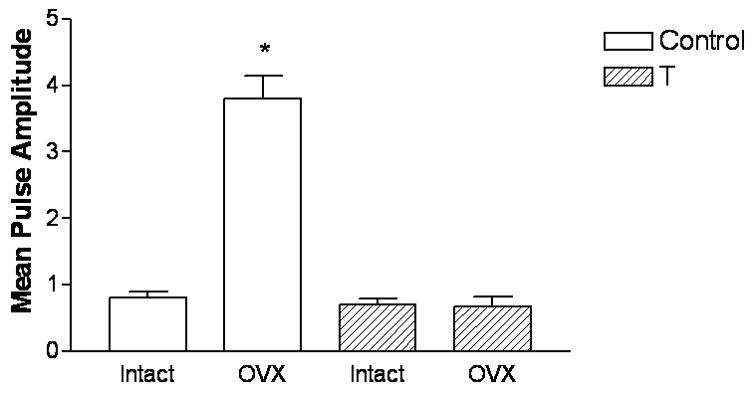
Female rat pups were subcutaneously injected with oil or 2.5 mg of testosterone propionate on the day of birth. On PND 60, rats were either ovariectomized (OVX) or sham-operated and left intact. Six days later, these rats were fitted with jugular catheters. The following day, blood samples were collected every 30 minutes for 3 hours from 1200h to 2100h. Serum LH levels were determined by RIA. Both mean LH levels (ng/ml) and mean pulse amplitude of LH was significantly increased (*p<0.001) by ovariectomy in control-treated females as compared to the SHAM control group (SHAM, n=3; OVX, n=5). Ovariectomy did not alter LH levels or pulse amplitude in the T-treated (n=5 for both groups) females.
