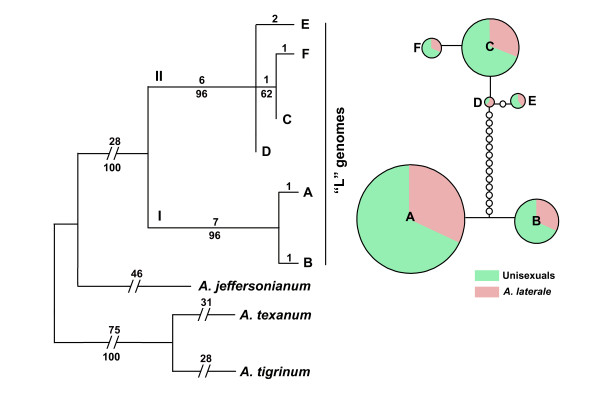
Figure 3.
Maximum parsimony tree (left) and TCS analysis (right) for six L-G1C12 haplotypes recovered from populations of Ambystoma laterale and unisexuals. For the MP tree, the outgroup species are A. jeffersonianum,A. texanum, and A. tigrinum. Taxa are haplotypes (A-F). Numbers above the branches represents numbers of mutations, and below depicts bootstrap values greater than 50. There is a distinct genetic break between clade I [A, B] and clade II [C, D, E, F]. For the TCS haplotype network, haplotypes A-F are represented by circles whose areas are proportional to the frequencies of the particular haplotype. The relative frequencies of unisexuals vs A. laterale partitioned in each particular haplotype are shown by different colors (green and pink respectively). Small and empty circles represent intermediate haplotypes that are not present in the samples but are necessary to link all observed haplotypes to the network. All haplotypes are separated from the nearest haplotype by one nucleotide difference. A distinct genetic break (13 transitional steps) between [A, B] and [C, D, E, F] is identified by TCS.