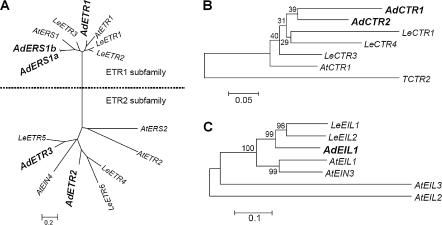
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of AdETRs (A), AdCTRs (B), and AdEIL1 (C). The amino acid sequences were analysed with Vector NTI (v. 9.0.0, Invitrogen) and the phylogenetic tree constructed with MEGA (v. 3.1) using a bootstrap test of phylogeny with minimum evolution test and default parameters. The amino acid sequences of Arabidopsis and tomato were obtained from the NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) database, and accession numbers are as follows: AtETR1 (AAA70047), AtERS1 (NP_181626), AtETR2 (NP_188956), AtERS2 (AAC62209), AtEIN4 (AAD02485), AtCTR1 (AAA32780), AtEIN3 (NP_188713), AtEIL1 (NP_180273), AtEIL2 (NP_197611) and AtEIL3 (NP_177514) in Arabidopsis; LeETR1 (AAC02213), LeETR2 (AAC02214), LeETR3 (AAC49124), LeETR4 (AAU34076), LeETR5 (AAD31397), LeETR6 (AAL86614), LeCTR1 (AAL87456), TCTR2 (CAA06334), LeCTR3 (AAR89820), LeCTR4 (AAR89822), LeEIL1 (AAK58857) and LeEIL2 (AAK58858) in tomato.