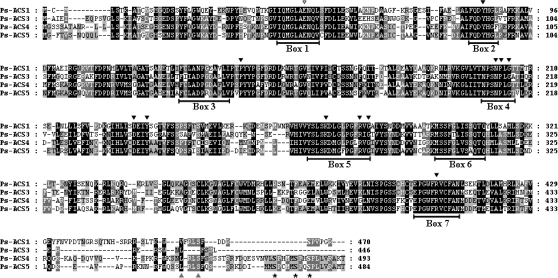
Fig. 1.
Amino acid sequence alignment of Ps-ACS1 (EU034649), Ps-ACS3 (EU034650), Ps-ACS4 (EU034653), and Ps-ACS5 (EU034654) using the ClustalX program. Conserved residues are shaded in black. Dark grey shading indicates similar residues in three out of four of the sequences and light grey shading indicates similar residues in two out of four of the sequences. The 11 black arrows designate the residues that represent the conserved amino acids in aminotransferases. The conserved glutamate residue (E) marked with an open arrow is involved in substrate specificity (McCarthy et al., 2001). The two grey arrows indicated the Val and Ser residues important for interaction with ETO1 and CDPK phosphorylation (Tatsuki and Mori, 2001; Yoshida et al., 2005). The Ser residues that are targets of the protein kinase MPK6 phosphorylation (Liu and Zhang, 2004) are marked with asterisks.