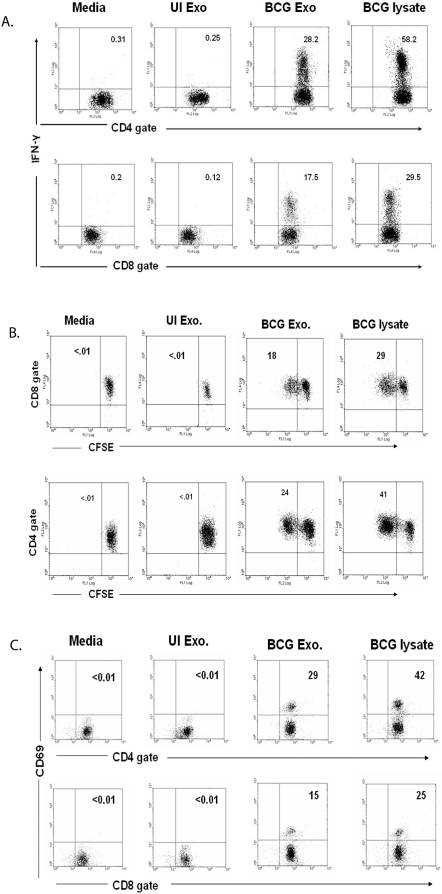
Figure 1. Activation of BCG sensitized splenic T cells by exosomes from BCG-infected macrophages.
Balb/C mice were infected with BCG (1×106/mouse). Four weeks post-infection, splenocytes were harvested. (A) Splenocytes from BCG infected mice were cultured with BCG or UI exosomes, BCG lysate or media. 12 hr post-treatment, cells were stained with anti-CD4-PE, anti-CD8-PE-Cy5 and anti-IFN-γ-FITC and analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) Splenocytes from BCG infected mice, labeled with 2.5 µM CFSE, were treated with BCG or UI exosome, BCG lysate or media. 72 hr post-treatment, cells were stained with anti-CD4-PE or anti-CD8-PE-Cy5 and analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) Splenocytes from BCG infected mice were cultured with BCG or UI exosomes, BCG lysate or media. 72 hr post-treatment, cells were stained with anti-CD4-PE, anti-CD8-FITC and anti-CD69-PE-Cy5 and analyzed by flow cytometry. Total lymphocytes were gated using FSC/SSC. CFSE, CD69 and intracellular IFN-γ levels were detected on gated CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes. Results are shown as percent positive. Cells were negative for staining with isotype control antibodies. Results are representative of at least 3 independent experiments.