Abstract
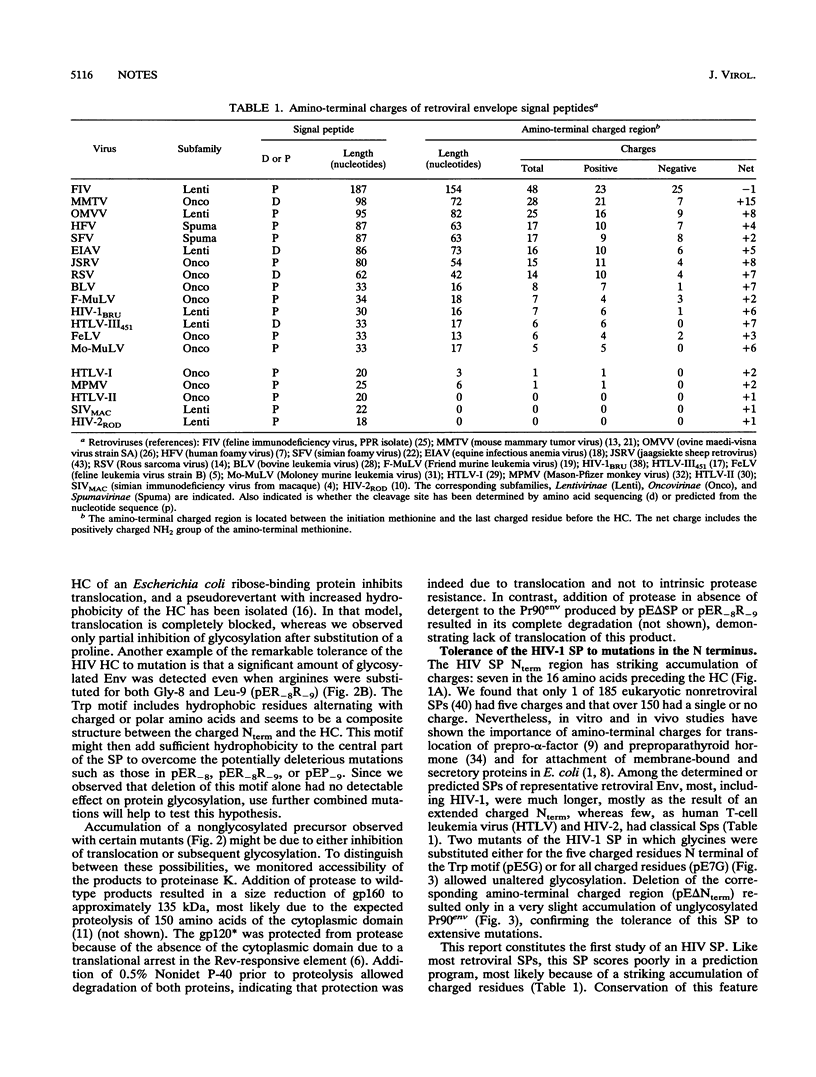
We demonstrated that the leader sequence of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope functions as signal peptide (SP) despite low scoring in a prediction program. As expected for SP, the hydrophobic core (HC) is essential, and no other sequence could compensate for HC deletion. Contrary to other SPs, major substitutions in the HC, such as introduction of basic, polar, or alpha-helix-breaking residues, still allowed efficient translocation and glycosylation. Also, extensive deletions or substitutions of the charged residues at the N terminus had little if any inhibitory effect. This report, which is the first study of human immunodeficiency virus SP, describes the exceptional tolerance of this peptide to mutations.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akita M., Sasaki S., Matsuyama S., Mizushima S. SecA interacts with secretory proteins by recognizing the positive charge at the amino terminus of the signal peptide in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8164–8169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison D. S., Young E. T. Single-amino-acid substitutions within the signal sequence of yeast prepro-alpha-factor affect membrane translocation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1915–1922. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti L., Guyader M., Alizon M., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., Tiollais P., Sonigo P. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from macaque and its relationship to other human and simian retroviruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):543–547. doi: 10.1038/328543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Mullins J. I. Nucleotide sequence of the envelope gene of Gardner-Arnstein feline leukemia virus B reveals unique sequence homologies with a murine mink cell focus-forming virus. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):871–880. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.871-880.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügel R. M., Rethwilm A., Maurer B., Darai G. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the env gene and its flanking regions of the human spumaretrovirus reveals two novel genes. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2077–2084. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02473.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallusser A., Kuhn A. Initial steps in protein membrane insertion. Bacteriophage M13 procoat protein binds to the membrane surface by electrostatic interaction. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2723–2729. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07459.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R., Kramer R. A., Shields D. Misplacement of the amino-terminal positive charge in the prepro-alpha-factor signal peptide disrupts membrane translocation in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2963–2968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyader M., Emerman M., Sonigo P., Clavel F., Montagnier L., Alizon M. Genome organization and transactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):662–669. doi: 10.1038/326662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffar O. K., Dowbenko D. J., Berman P. W. Topogenic analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein, gp160, in microsomal membranes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1677–1687. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Sowder R., Smythers G., Oroszlan S. Terminal amino acid sequences and proteolytic cleavage sites of mouse mammary tumor virus env gene products. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):314–319. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.314-319.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. A., Michel H., Sakaguchi K., Shabanowitz J., Appella E., Hunt D. F., Engelhard V. H. HLA-A2.1-associated peptides from a mutant cell line: a second pathway of antigen presentation. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1264–1266. doi: 10.1126/science.1546329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter E., Hill E., Hardwick M., Bhown A., Schwartz D. E., Tizard R. Complete sequence of the Rous sarcoma virus env gene: identification of structural and functional regions of its product. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):920–936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.920-936.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahimi I., Gentz R. A functional interaction between the signal peptide and the translation apparatus is detected by the use of a single point mutation which blocks translocation across mammalian endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10189–10194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida A., Groarke J. M., Park S., Thom J., Zabicky J. H., Hazelbauer G. L., Randall L. L. A signal sequence mutant defective in export of ribose-binding protein and a corresponding pseudorevertant isolated without imposed selection. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1875–1880. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03863.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalyanaraman V. S., Rodriguez V., Veronese F., Rahman R., Lusso P., DeVico A. L., Copeland T., Oroszlan S., Gallo R. C., Sarngadharan M. G. Characterization of the secreted, native gp120 and gp160 of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Mar;6(3):371–380. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami T., Sherman L., Dahlberg J., Gazit A., Yaniv A., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Nucleotide sequence analysis of equine infectious anemia virus proviral DNA. Virology. 1987 Jun;158(2):300–312. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Hunsmann G., Friedrich R. Nucleotide sequence of the envelope gene of Friend murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.1-9.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J. E., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequencing of an apparent proviral copy of env mRNA defines determinants of expression of the mouse mammary tumor virus env gene. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):495–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.495-504.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergia A., Shaw K. E., Lackner J. E., Luciw P. A. Relationship of the env genes and the endonuclease domain of the pol genes of simian foamy virus type 1 and human foamy virus. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):406–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.406-410.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngsee J. K., Hansen W., Walter P., Smith M. Cassette mutagenic analysis of the yeast invertase signal peptide: effects on protein translocation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3400–3410. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nothwehr S. F., Gordon J. I. Structural features in the NH2-terminal region of a model eukaryotic signal peptide influence the site of its cleavage by signal peptidase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17202–17208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips T. R., Talbott R. L., Lamont C., Muir S., Lovelace K., Elder J. H. Comparison of two host cell range variants of feline immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4605–4613. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4605-4613.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Querat G., Audoly G., Sonigo P., Vigne R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of SA-OMVV, a visna-related ovine lentivirus: phylogenetic history of lentiviruses. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):434–447. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90428-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. P., Duncan M. C., Bankaitis V. A., Bassford P. J., Jr Intragenic reversion mutations that improve export of maltose-binding protein in Escherichia coli malE signal sequence mutants. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3389–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Yasunaga T., Tsuzuku-Kawamura J., Ohishi K., Ogawa Y., Ikawa Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of the genome of bovine leukemia virus: its evolutionary relationship to other retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):677–681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Hattori S., Hirayama Y., Yoshida M. Human adult T-cell leukemia virus: complete nucleotide sequence of the provirus genome integrated in leukemia cell DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3618–3622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Takahashi Y., Shimizu N., Gojobori T., Golde D. W., Chen I. S., Miwa M., Sugimura T. Complete nucleotide sequence of an infectious clone of human T-cell leukemia virus type II: an open reading frame for the protease gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3101–3105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonigo P., Barker C., Hunter E., Wain-Hobson S. Nucleotide sequence of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus: an immunosuppressive D-type retrovirus. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90323-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stader J., Benson S. A., Silhavy T. J. Kinetic analysis of lamB mutants suggests the signal sequence plays multiple roles in protein export. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15075–15080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczesna-Skorupa E., Mead D. A., Kemper B. Mutations in the NH2-terminal domain of the signal peptide of preproparathyroid hormone inhibit translocation without affecting interaction with signal recognition particle. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8896–8900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wain-Hobson S., Sonigo P., Danos O., Cole S., Alizon M. Nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, LAV. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Lingappa V. R. Mechanism of protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:499–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills J. W., Hardwick J. M., Shaw K., Hunter E. Alterations in the transport and processing of Rous sarcoma virus envelope glycoproteins mutated in the signal and anchor regions. J Cell Biochem. 1983;23(1-4):81–94. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240230109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- York D. F., Vigne R., Verwoerd D. W., Querat G. Isolation, identification, and partial cDNA cloning of genomic RNA of jaagsiekte retrovirus, the etiological agent of sheep pulmonary adenomatosis. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):5061–5067. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.5061-5067.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Analysis of the distribution of charged residues in the N-terminal region of signal sequences: implications for protein export in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2315–2318. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02132.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. How signal sequences maintain cleavage specificity. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 25;173(2):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





