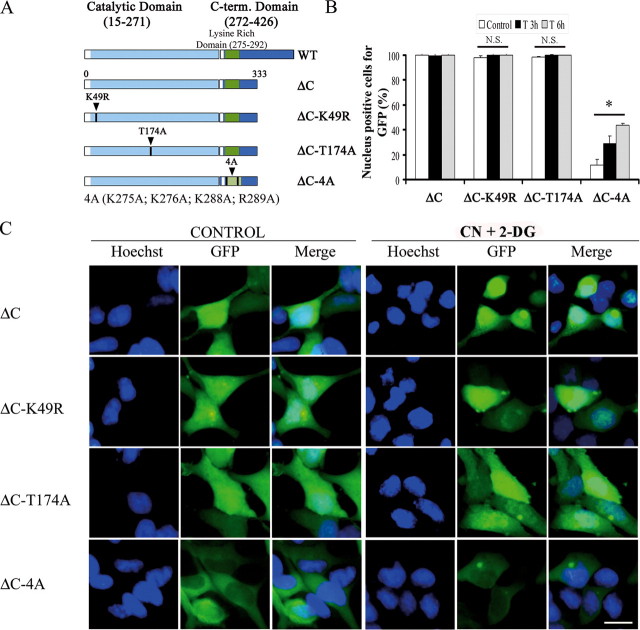
FIGURE 8.
An N-terminal fragment of SOK1 can enter the nucleus in a constitutive manner independently of its kinase activity but dependent on amino acids 275-292. HEK293 cells were transfected with GFP-SOK1ΔC (bearing amino acids 1-331 of SOK1) fusion protein or with the mutants SOK1ΔCK49R, SOK1ΔCT174A, and SOK1ΔC4A. 24 h after transfection cells were incubated with sodium cyanide and 2-deoxyglucose or left untreated (control). A, schematic representation of the mutants used in this study. B, percentage of cells in which the different mutants of GFP-SOK1 show a nuclear signal. At least 100 GFP-positive cells per mutant and time point were scored for GFP nuclear positivity. Shown is the average and S.D. of the percentage of cells positive for nuclear GFP from at least four independent experiments. C, control; T3 and T6, 3 and 6 h after treatment. p > 0.05 (N.S.) and p < 0.05 (*) versus SOK1ΔC. C, images of representative fields of control and treated cells transfected with the different GFP-SOK1 mutants in control cells and cells treated for 6 h. The bar represents 10 μm. CN+2-DG, sodium cyanide and 2-deoxyglucose.