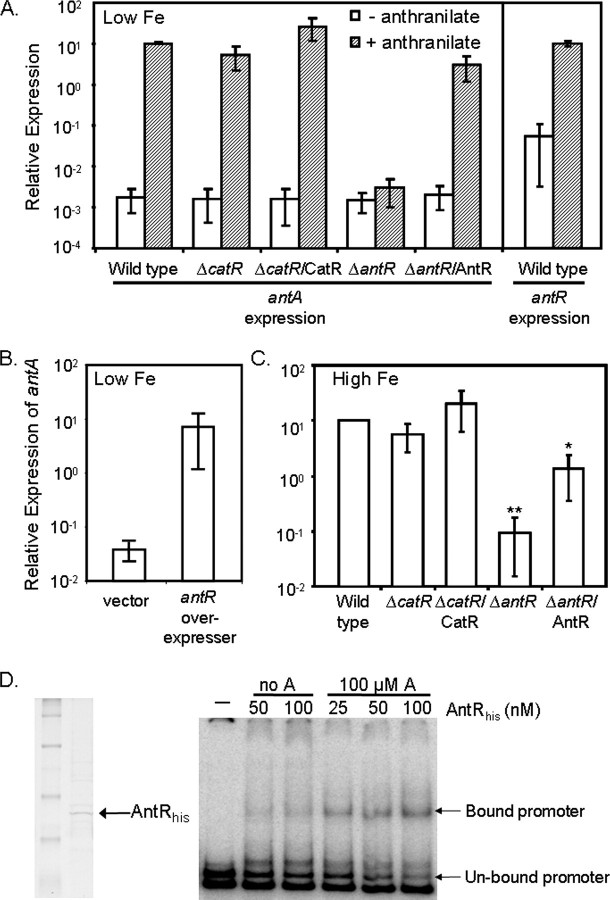
FIGURE 3.
Role of anthranilate, AntR, and CatR in the regulation of antA. A–C, RT-PCR was used to measure expression of antA and antR mRNA from the indicated strains grown at 37 °C for 18 h in DTSB, with or without iron or anthranilate supplementation as indicated. Low Fe, low iron. B, for the effects of antR overexpression, strain PAO1 carrying either pUCP18 or pUCP-antR was grown at 37 °C for 18 h in DTSB supplemented with 100μm IPTG to induce antR expression. Error bars show the standard deviation of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *, p < 0.05 between ΔantR/AntR and ΔantR by Student's t test. **, p < 0.0001 between ΔantR and wild type by Student's t test. High Fe, high iron. D, His-tagged AntR was purified over a nickel column as described under “Experimental Procedures,” dialyzed, concentrated, and run on an SDS-PAGE gel. Purified AntR was hybridized to the labeled antR promoter in the presence (A) or absence (no A) of anthranilate as indicated. The resulting hybridization reactions were run on a non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel. The arrows point to the shifted antR promoter fragments.