FIGURE 3.
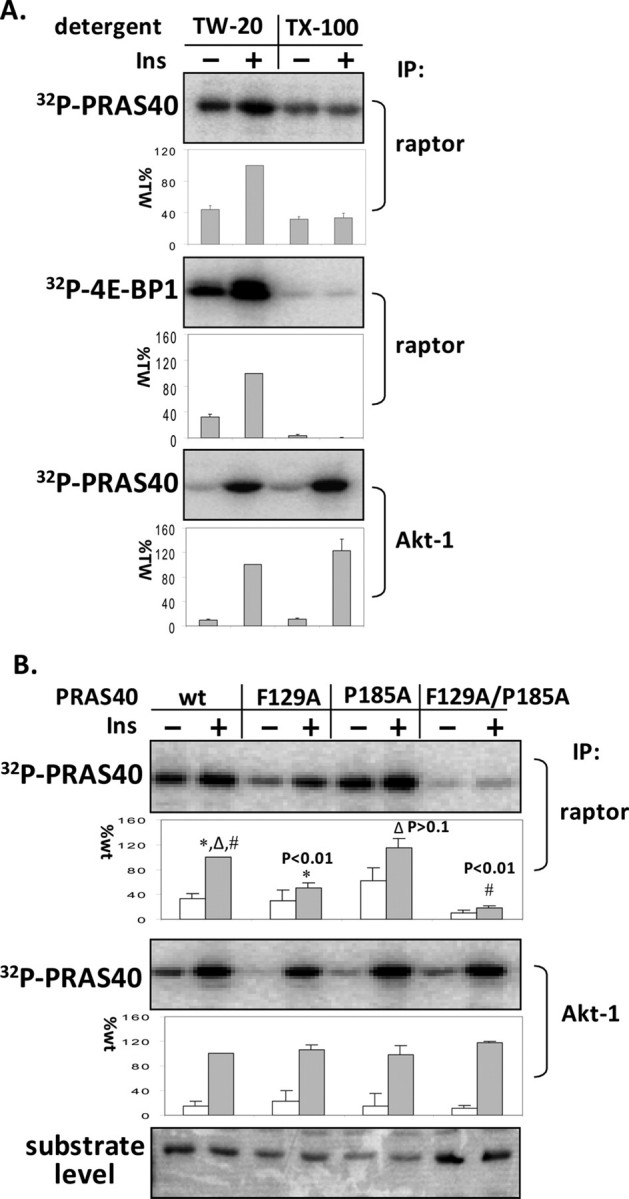
Disassociation of mTOR and raptor by Triton X-100 and disruption of the TOS motif in PRAS40 are unable to eliminate phosphorylation of PRAS40. 3T3-L1 adipocytes were incubated with insulin (60 nm) for 30 min. A, mTORC1 and Akt1 were isolated from adipocyte extracts in the presence of 0.2% Tween 20 by using raptor and Akt1 antibodies. The indicated detergents (0.2% final concentration) were added to the washed complexes, which were then incubated with [γ-32P]ATP and PRAS40 or 4E-BP1. 32P-Labeled PRAS40 and 4E-BP1 were detected by phosphorimaging. The amounts of incorporated 32P in PRAS40 and 4E-BP1 relative to the level of phosphorylation in the presence of Tween 20 with insulin treatment (%TW) were determined (mean ± S.E. from three experiments). TW-20, Tween 20; TX-100, Triton X-100. B, mTORC1 and Akt1 kinase assays were conducted using PRAS40 wild type (wt) and the indicated mutative proteins as substrates. The effect on 32P incorporation into PRAS40 (corrected for substrate level) is expressed as a percentage relative to wild type (mean ± S.E. from three experiments), and a t test was conducted between wild type and mutants. IP, immunoprecipitation.
