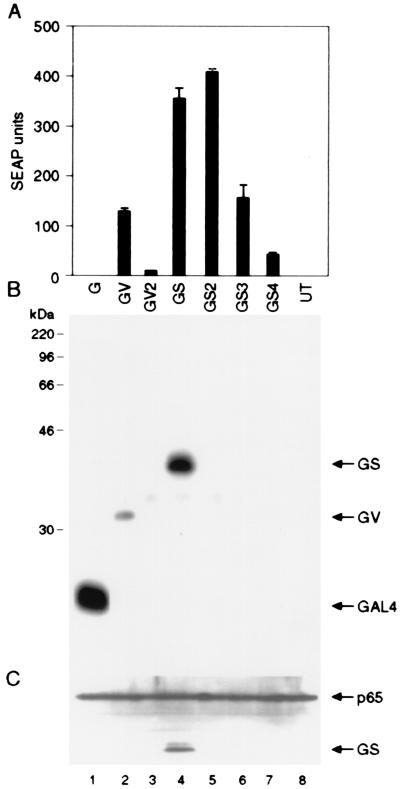
Figure 1.
Multimerization of potent activation domains increases their specific activity but decreases their intracellular concentration. (A) Indicated GAL4 activator plasmids (100 ng each) were introduced into HT1080B cells that carry a stably integrated SEAP reporter gene placed under the control five GAL4-binding sites. Recombinant proteins GV and GV2 contain GAL4 DNA-binding domains fused with one and two copies of VP16 activation domains. GS, GS2, GS3, and GS4 contain GAL4 DNA-binding domains fused with one, two, three, and four copies of p65 activation domains, respectively. G denotes the GAL4 DNA-binding domain only. Mean values of the SEAP activity secreted into the medium are shown (±SD). (B and C) Western blot analysis of the total cellular extracts from transfected cells. The membrane was probed first with anti-hemagglutinin to detect the transfected proteins (B) and then with anti-p65 antibodies to confirm that roughly equal amounts of protein are present in each lane (C).