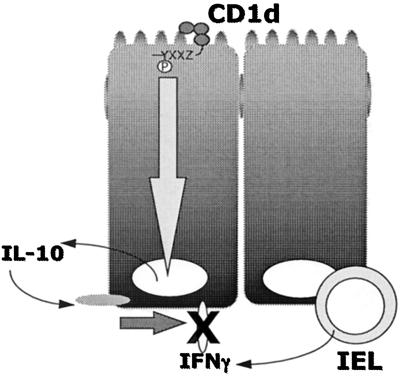
Figure 5.
Proposed model of CD1d signaling in polarized intestinal epithelia. Results from these studies define a signal transduction pathway through surface activation of epithelial CD1d and illustrate that this pathway may serve to dampen proinflammatory signals at the level of mucosal epithelia through the autocrine actions of epithelial-cell-derived IL-10.