FIGURE 1.
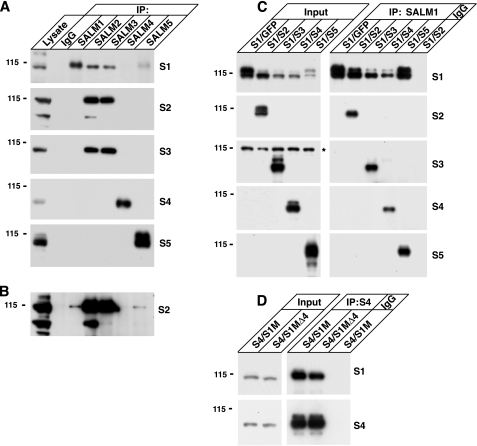
SALMs form complexes in brain and heterologous cells. A, rat forebrain (P15) was solubilized with 1% deoxycholate. Proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-SALM 1–5 antibodies or control IgG and probed with anti-SALM antibodies (SALM1–SALM5 = S1–S5). SALMs 1–3 form heteromeric complexes in brain. SALMs 4 and 5 do not strongly co-immunoprecipitate with SALMs 1–3 from rat brain lysate, suggesting that SALMs 4 and 5 may function as homomeric complexes in brain. B, a longer exposure time of the second panel in A indicates that SALM2 also co-immunoprecipitates with SALM1 and SALM5, but not as abundantly as its association with SALM3. C, SALM1 was co-transfected with SALMs 2–5 in HEK293 cells (transfections shown in columns above the panel; input = immunoblots of the lysates). Proteins were solubilized with RIPA buffer and immunoprecipitated with anti-SALM1 antibodies or control rabbit IgG. Blots were then probed with anti-SALM 1–5. SALMs 2–5 co-immunoprecipitate with SALM1, indicating that all the SALMs can form heteromeric complexes when expressed together in HEK293 cells (asterisk indicates a nonspecific band). D, Myc-SALM1 (S1M) or Myc-SALM1Δ4 (S1MΔ4), which we have previously shown is not expressed on the cell surface (11), were co-transfected with SALM4. Both co-immunoprecipitate with SALM4, suggesting that SALM1 can form a complex with SALM4 within intracellular compartments.