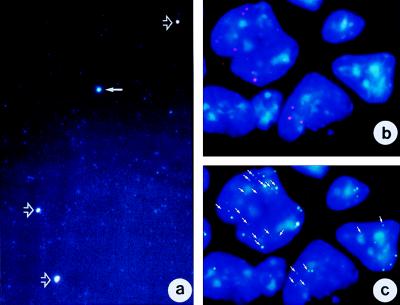
Figure 4.
The EEs are functional genetic units. (a) Purified extrachromosomal DNA molecules were immunostained with anti-histone antibodies. EEs are counterstained with DAPI and, therefore, appear blue. Immunostaining with the pan-histone antibody appears green, whereas the anti-histone-H3P-stained targets appear red. Thus, EEs immunostained with pan-histone antibody plus DAPI appear greenish-whitish, whereas those stained with histone H3P plus DAPI appear reddish. When histone H3P and pan-histone colocalize on the same EE, the color overlay is yellowish. The image shows four large EEs (arrows) that are surrounded by a group of small EEs. The small EEs stain with DAPI only. A pan-histone-immunostained EE is shown by a solid arrow. Three EEs indicated with open arrows show colocalization of anti-pan-histone (green) and anti-histone H3P (red) antibodies. (b) mRNA track study of c-myc in DCPC21 PCT cells. Red signals represent mRNA tracks produced in the cells. The tracks are short, as expected, from extrachromosomal DNA or episomes. (c) FISH analysis of the sample shown in b. The c-myc gene was labeled with digoxigenin and visualized with an anti-digoxigenin-FITC antibody (Materials and Methods). Arrows point to those c-myc-carrying EEs (green) that also transcribe c-myc (compare b and c). Note that not all c-myc-bearing EEs are transcribing c-myc.