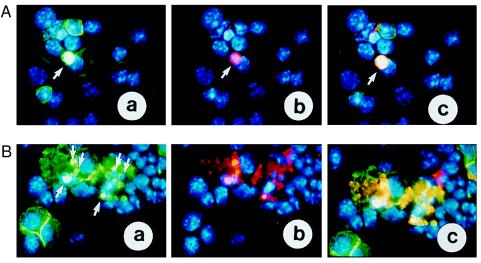
Figure 5.
Extrachromosomal gene transfer studies. Purified EEs were electroporated into primary spleen cells along with a GFP-expressing vector that served as a tracer molecule for gene transfer efficiency. B220 was used as a cell surface marker for splenic B lymphocytes. (A) GFP and c-Myc expression in primary B cells 24 hr after electroporation: (a) B220-positive primary B cells as revealed by the FITC-conjugated (green) antibody on the membrane. The arrow points to a B cell expressing GFP. The greenish-whitish color is due to the overlay of the nuclear staining with DAPI (blue) and GFP (green). (b) The B220-positive B cell that shows GFP expression also overexpresses c-Myc protein (red) (see arrow). (c) Overlay of image a and b: the orange nucleus shown expresses GFP and c-Myc (see arrow). (B) Ninety percent of the electroporated primary B cells die 24 hr after transfer of EEs: (a) GFP expression in B220-positive B cells. (b) c-Myc-expression in B220-positive B cells. (c) Overlay of a and b: the GFP-positive and B220-positive primary B cells that overexpress electroporated c-Myc die. Arrows point to some of the apoptotic bodies that form in these cells.