Abstract
Some of the more important recent studies on the effect of thiazides and beta-adrenoceptor blocking agents is conflicting, possibly because of differences in patient compliance and in lipoprotein methodology and quality assurance between studies. It is likely that in the short-term, thiazide diuretics produce an increase in plasma triglyceride and cholesterol and in LDL-cholesterol. No consistent effect of monotherapy with beta-adrenoceptor blocking agents was seen. Further long-term studies of monotherapy with both of these classes of drugs are required. Combined therapy with thiazides or beta-adrenoceptor blocking agents consistently increased plasma triglyceride concentrations, but their effect on VLDL, LDL and HDL concentrations is uncertain. Further research required into the effect of these drugs on apolipoproteins which may be useful discriminators for patients with coronary heart disease (Avogaro et al., 1979) and on HDL subfractions.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
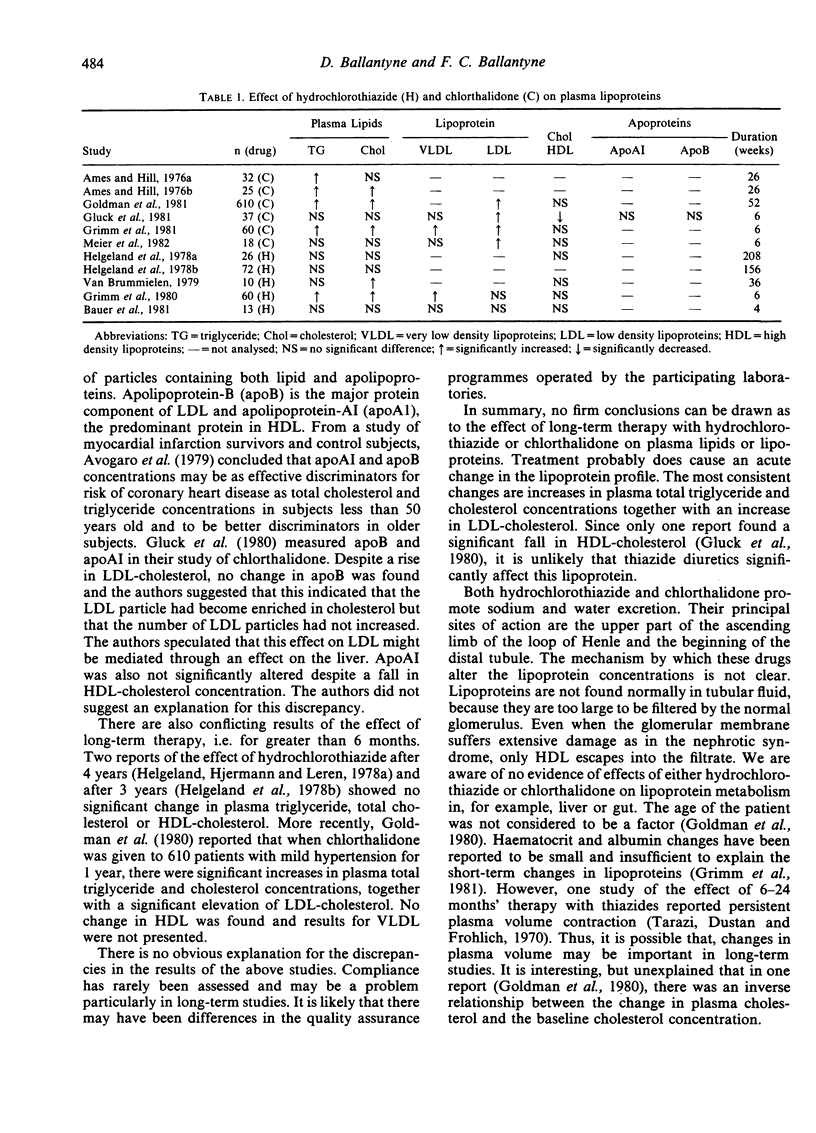
- Ames R. P., Hill P. Elevation of serum lipid levels during diuretic therapy of hypertension. Am J Med. 1976 Nov;61(5):748–757. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90156-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames R. P., Hill P. Increase in serum-lipids during treatment of hypertension with chlorthalidone. Lancet. 1976 Apr 3;1(7962):721–723. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)93093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avogaro P., Bon G. B., Cazzolato G., Quinci G. B. Are apolipoproteins better discriminators than lipids for atherosclerosis? Lancet. 1979 Apr 28;1(8122):901–903. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91375-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
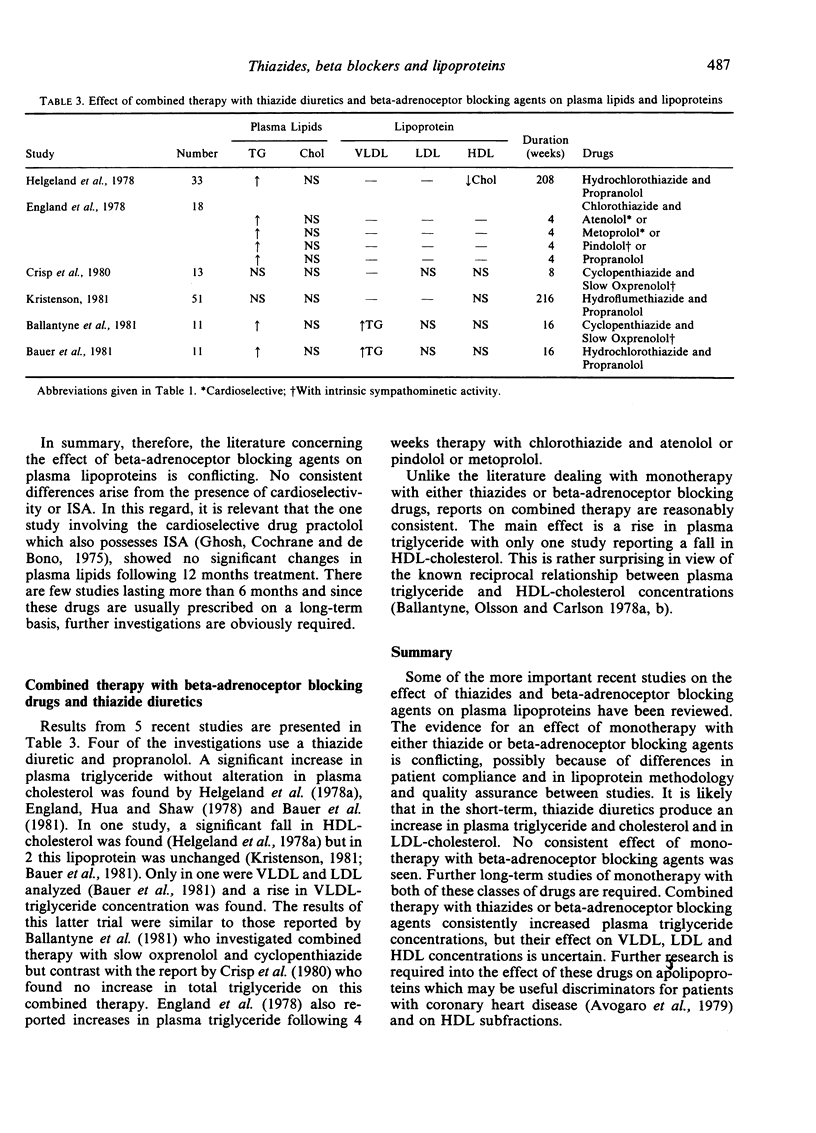
- Ballantyne D., Ballantyne F. C., McMurdo Effect of slow oxprenolol and a combination of slow oxprenolol and cyclopenthiazide on plasma lipoproteins. Atherosclerosis. 1981 Jun;39(3):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(81)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantyne D., Grossart K. W., Ballantyne J. P., Young A., Lawrie T. D. Relationship of plasma lipids and lipoprotein concentration to cerebral atherosclerosis and electrocardiographic findings. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Oct;23(2):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90234-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantyne F. C., Clark R. S., Simpson H. S., Ballantyne D. High density and low density lipoprotein subfractions in survivors of myocardial infarction and in control subjects. Metabolism. 1982 May;31(5):433–437. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90230-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
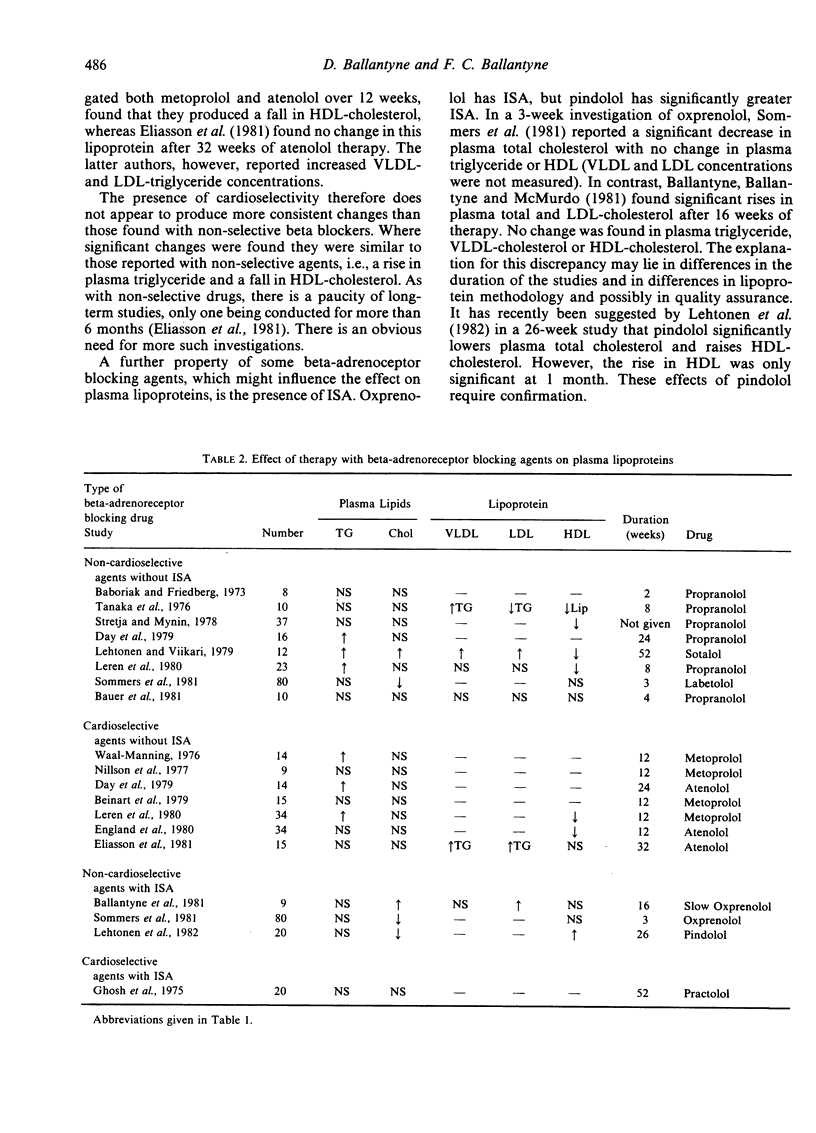
- Barboriak J. J., Friedberg H. D. Propranolol and hypertriglyceridemia. Atherosclerosis. 1973 Jan-Feb;17(1):31–35. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(73)90132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer J. H., Brooks C. S., Weinstein I., Wilcox H. H., Heimberg M., Burch R. N., Barkley R. Effects of diuretic and propranolol on plasma lipoprotein lipids. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Jul;30(1):35–43. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beinart I. W., Cramp D. G., Pearson R. M., Havard C. W. The effect of metoprolol on plasma lipids. Postgrad Med J. 1979 Oct;55(648):709–711. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.55.648.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crisp A. J., Kennedy P. G., Hoffbrand B. I., Ebbutt A. F., Carruthers M. Lipids and lipoprotein fractions after cyclopenthiazide and oxprenolol: a double-blind crossover study. Curr Med Res Opin. 1980;7(2):101–103. doi: 10.1185/03007998009112034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day J. L., Simpson N., Metcalfe J., Page R. L. Metabolic consequences of atenolol and propranolol in treatment of essential hypertension. Br Med J. 1979 Jan 13;1(6156):77–80. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6156.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliasson K., Lins L. E., Rössner S. Serum lipoprotein changes during atenolol treatment of essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1981;20(5):335–338. doi: 10.1007/BF00615401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England J. D., Simons L. A., Gibson J. C., Carlton M. The effect of metoprolol and atenolol on plasma high density lipoprotein levels in man. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1980 May-Jun;7(3):329–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1980.tb00078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P., Cochrane A. M., de Bono D. Effects of long-term practolol therapy on plasma-lipids after acute myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1975 Jan 4;1(7897):9–10. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glück Z., Weidmann P., Mordasini R., Bachmann C., Riesen W., Peheim E., Keusch G., Meier A. Increased serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in men treated short-term with the diuretic chlorthalidone. Metabolism. 1980 Mar;29(3):240–245. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman A. I., Steele B. W., Schnaper H. W., Fitz A. E., Frohlich E. D., Perry H. M., Jr Serum lipoprotein levels during chlorthalidone therapy. A Veterans Administration-National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute cooperative study on antihypertensive therapy: mild hypertension. JAMA. 1980 Oct 10;244(15):1691–1695. doi: 10.1001/jama.244.15.1691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm R. H., Jr, Leon A. S., Hunninghake D. B., Lenz K., Hannan P., Blackburn H. Effects of thiazide diuretics on plasma lipids and lipoproteins in mildly hypertensive patients: a double-blind controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jan;94(1):7–11. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-1-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgeland A., Hjermann I., Holme I., Leren P. Serum triglycerides and serum uric acid in untreated and thiazide-treated patients with mild hypertension. The Oslo study. Am J Med. 1978 Jan;64(1):34–38. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgeland A., Hjermann I., Leren P., Enger S., Holme I. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and antihypertensive drugs: the Oslo study. Br Med J. 1978 Aug 5;2(6134):403–403. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6134.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannel W. B., Castelli W. P., Gordon T. Cholesterol in the prediction of atherosclerotic disease. New perspectives based on the Framingham study. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Jan;90(1):85–91. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen B. O. Effect of long-term treatment with beta-blocking drugs on plasma lipids and lipoproteins. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Jul 18;283(6285):191–192. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6285.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtonen A., Hietanen E., Marniemi J., Peltonen P., Niskanen J. Effect of pindolol on serum lipids and lipid metabolizing enzymes. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982;13(Suppl 2):445S–447S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01955.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier A., Weidmann P., Mordasini R., Riesen W., Bachmann C. Reversal or prevention of diuretic-induced alterations in serum lipoproteins with betablockers. Atherosclerosis. 1982 Feb;41(2-3):415–419. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(82)90205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motulsky H. J., Insel P. A. Adrenergic receptors in man: direct identification, physiologic regulation, and clinical alterations. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jul 1;307(1):18–29. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198207013070104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson A., Hansson B. G., Hökfelt B. Beta-blockers and lipid metabolism. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 9;2(6079):126–126. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6079.126-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOENFELD M. R., GOLDBERGER E. HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA INDUCED BY THIAZIDES: A PILOT STUDY. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1964 Mar;6:180–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith U. Adrenergic control of human adipose tissue lipolysis. Eur J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;10(5):343–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1980.tb00042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommers D. K., de Villiers L. S., van Wyk M., Schoeman H. S. The effects of labetalol and oxprenolol on blood lipids. S Afr Med J. 1981 Sep 5;60(10):379–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streja D., Mymin D. Effect of propranolol on HDL cholesterol concentrations. Br Med J. 1978 Nov 25;2(6150):1495–1495. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6150.1495-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Sakaguchi S., Oshige K., Niimura T., Kanehisa T. Effect of chronic administration of propranolol on lipoprotein composition. Metabolism. 1976 Oct;25(10):1071–1075. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waal-Manning H. J. Metabolic effects of beta-adrenoreceptor blockers. Drugs. 1976;11(Suppl 1):121–126. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197600111-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. E., Simpson E. R. Inhibition of the lipolytic action of beta-adrenergic agonists in human adipocytes by alpha-adrenergic agonists. J Lipid Res. 1981 Nov;22(8):1265–1270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Brummelen P., Gevers Leuven J. A., van Gent C. M. Influence of hydrochlorothiazide on the plasma levels of triglycerides, total cholesterol and HDL-cholesterol in patients with essential hypertension. Curr Med Res Opin. 1979;6(1):24–29. doi: 10.1185/03007997909109394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


