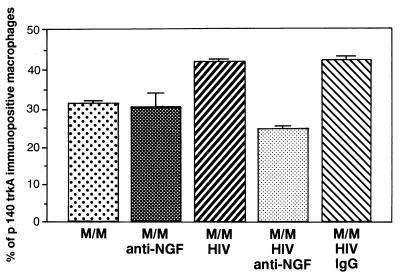
Figure 2.
Expression of high-affinity receptors on macrophages infected by HIV. Treatment of HIV-infected M/M with anti-NGF Ab (M/M + HIV + anti-NGF), but not with an IgG isotypic Ab (M/M + HIV + IgG), modifies the cellular expression of p140 trkA high-affinity receptor. Quantitative analysis of p140 trkA-immunoreactive cells carried out with a computerized image-analysis system (Zeiss Axiophot 2 microscope equipped with a Vidas Kontron system) shows that the increase of p140 trkA immunopositive cells in HIV-infected human M/M (M/M + HIV) was statistically significant (ANOVA: F(4, 85) = 116.017; P < 0.01) compared with mock-infected human M/M (M/M). Treatment of HIV-infected M/M with anti-NGF Ab (M/M + HIV + anti-NGF) yielded a statistically significant decrease (P < 0.01) of p140 trkA immunoreactivity in comparison to HIV-infected M/M (M/M + HIV), mock-infected human M/M (M/M + anti-NGF), or HIV-infected M/M with an irrelevant IgG Ab (M/M + HIV + IgG).