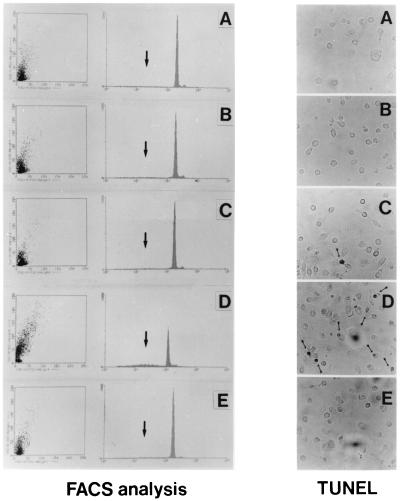
Figure 4.
Programmed cell death in HIV-infected macrophages exposed to anti-NGF Ab. (Left) FACS analysis. Apoptosis was detected by DNA labeling with propidium iodide, a fluorescent intercalating dye that allows DNA quantification. Apoptotic nuclei appeared as a broad hypodiploid DNA peak (black arrow in each panel) easily discriminable from the narrow peak of nuclei with normal diploid DNA counted in the red fluorescence channel. DNA fragmentation has been detected in 5% of mock-infected human M/M (A). Results in the same range were observed in HIV-infected M/M (9.1% of propidium-positive cells; B), in mock-infected M/M exposed to anti-NGF Ab (6.9%; C), or in HIV-infected M/M treated with the IgG isotypic Ab (8.7%; E). By contrast, exposure of HIV-infected cells to anti-NGF Ab (D) induces DNA fragmentation in 40.3% of M/M in this experiment representative of five different tests. (Right) TUNEL. Immunocytochemical studies performed by TUNEL show nuclei with round condensed chromatin in HIV-infected M/M exposed to anti-NGF Ab (D) far more than in any of the other M/M samples tested (A, B, C, and E). The figure presents data from a typical experiment of three.