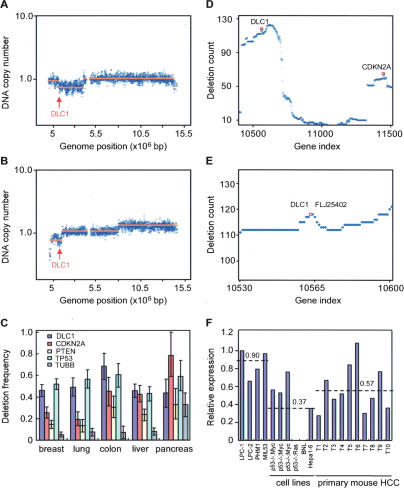
Figure 1.
DLC1 is a candidate tumor suppressor on chromosome 8p22. (A,B) DNA copy number profiles for chromosome 8 of two representative human HCC samples reveals chromosome 8p22 deletions containing DLC1. The blue data points represent the averaged fluorescent ratio (tumor vs. normal) and the orange lines correspond to the value determined by copy number segmentation. Arrows denote the DLC1 locus. (C) Deletion counts per case for DLC1, p16INK4a, PTEN, TP53, and β-Tubulin (TUBB) in five types of human carcinomas. The counts were obtained from ROMA profiles of 257 breast, 137 colon, 86 liver, 213 lung, and 46 pancreas cancers, respectively. β-Tubulin serves as a negative control. The error bars indicate the 90% confidence intervals for each quantity. (D) Deletion counts in ROMA profiles of 257 human breast cancers. A deletion count in each profile set was obtained by finding the maximal tier number for 24,719 genes across the genome in each profile in the set and summing the result over the set. The counts are plotted against the gene ordinal number, with the genes sorted by their genomic transcription start position. Shown is chromosome 8 and 9. The points in the vicinity of DLC1 and p16INK4A are highlighted by red circles. (E) High-magnification view of 8p22 region in D. DLC1 and FLJ25402 reside at a local deletion epicenter. FLJ25402 is an uncharacterized gene. (F) qPCR analysis of DLC1 expression in mouse embryonic liver progenitor cells (LPC), immortalized liver progenitor cells (MIL53 and PHM1), mouse HCC cells, and primary mouse HCC tumors. Numbers indicate the average value of each group.