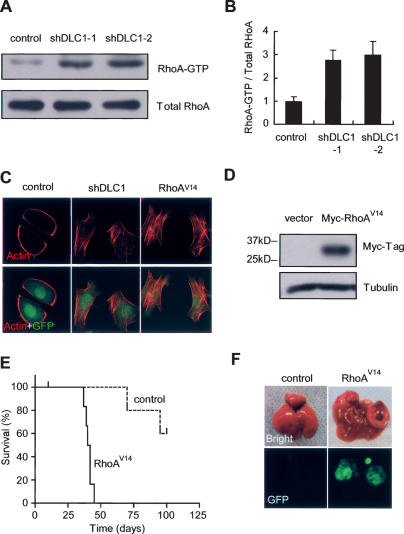
Figure 4.
DLC1 knockdown deregulates RhoA activity, which is sufficient to accelerate tumorigenesis. (A) RhoA-GTP pull-down assay of p53-null liver progenitor cells coinfected with Myc and a control shRNA or DLC1 shRNAs. (B) Quantification of A. Error bars denote SD (n = 3). (C) DLC1 knockdown increases actin stress fiber formation. p53−/−;Myc Liver progenitor cells infected with shDLC1 or RhoAV14 were serum starved and stained with fluorescent phalloidin. (D) Immunoblots of p53−/−-null hepatoblasts infected with Myc and a constitutively active RhoAV14 allele with 6xMyc tag at the N terminus. (E) Activated RhoA cooperates with Myc and loss of p53 to accelerate liver tumor formation. Kaplan-Meier survival curve of syngeneic mice transplanted with p53-null liver progenitor cells coinfected with Myc and RhoAV14 (n = 6 for each group). (F) Representative images of explanted livers at day 40 following cell transplantation. GFP imaging identifies retrovirally transduced cells.