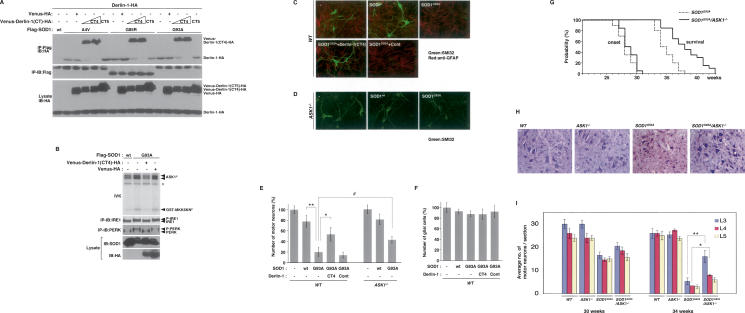
Figure 5.
Impairment of SOD1mut–Derlin-1 interaction and deletion of ASK1 mitigate SOD1mut-induced motor neurotoxicity. (A) Lysates from HEK293 cells, transfected at the indicated combinations, were analyzed by IP-IB. (B) NSC34 cells were infected with Ad-SOD1wt, Ad-SOD1G93A, Len-Venus-Derlin-1(CT4)-HA, and Len-Venus-HA at the indicated combinations for 48 h. Activation of IRE1 and PERK was examined as described in Figure 1A. Activation of ASK1 was analyzed by IVK using GST-MKK6KN as substrate. (ASK1P) Autophosphorylated ASK1. (GST-MKK6KNP) Phosphorylated GST-MKK6KN. Asterisk denotes nonspecific bands. (C) Wild-type mice spinal cord cultures were infected with lentivirus at the indicated combinations for 72 h. Cultures were fixed and doubly stained with antibodies to nonphosphorylated neurofilament (SMI32) (green) and GFAP (red). (D) ASK1−/− mice spinal cord cultures were infected as indicated and stained with SMI32 antibody. (E) The percentage of total cell count of SMI32 antibody-positive cells is shown compared with control culture (wild type; n = 3); (ASK1−/−; n = 5). Values are means ± SE of independent experiments. (*) P < 0.05; (**) P < 0.01; significance calculated by Student’s t-test. (#) P < 0.05 significance calculated by ANOVA. (F) The percentage of total cell count of anti-GFAP antibody-positive cells derived from wild-type mice is shown compared with control culture. Values are means ± SE of three independent experiments. (G) The onset of disease was determined by motor function deficit seen in rota-rod performance in SOD1G93A mice in the presence or absence (ASK1−/−) of ASK1. The cumulative probability of onset of rota-rod deficit was not significantly changed in SOD1G93A/ASK1−/− mice (n = 10; solid line) compared with SOD1G93A mice (n = 10; dotted line). Probabilities of survival reveal prolongation of life span of SOD1G93A/ASK1−/− mice (n = 20; solid line) compared with SOD1G93A mice (n = 20; dotted line). The data were analyzed by the Kaplan-Meier life test and by long-rank test. (H) Cresyl violet (Nissl)-stained paraffin sections of ventral horn from lumbar (level L3) spinal cords at end stage (age 34 wk) are shown. (I) Stereological analysis of motor neuron death. Numbers of motor neurons were determined by counting the large Nissl-positive neurons in the ventral horn. Five mice of each group were used for analysis. Thirty-week-old and 34-wk-old mice were sacrificed, and sections of lumbar spinal cord at levels L3, L4, and L5 were counted for each mouse. Values are means ± SE. (*) P < 0.05; (**) P < 0.01; significance calculated by Student’s t-test.