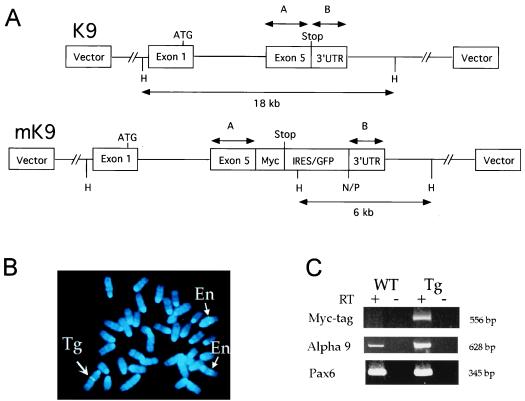
Figure 1.
(A) Site-directed mutagenesis of a BAC containing the mouse α9 AChR gene. In 13K9 (K9, 140 kb), a myc-tag was inserted before the stop codon in exon 5 of the α9 AChR gene, and an IRES/GFP cassette (1.3 kb) was inserted after the stop codon. Two homologous fragments, A (541 bp) and B (321 bp), which contain the coding portion and the 3′untranslated region (3′UTR) of exon 5, respectively, were used for modification of K9. The IRES/GFP cassette in modified K9 (mK9) contains additional NotI (N), PmeI (P), and HindIII (H) sites. Whereas exons 1–4 are intact, only exon 1 with the ATG start codon is depicted, for simplicity. (B) FISH analysis of metaphase embryonic fibroblast cells from transgenic mice by using K9 BAC DNA. Blue color (4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) staining represents each of 40 metaphase chromosomes. K9 BAC DNA hybridized (in green color) to two endogenous α9 AChR loci on two chromosomes 4 (thin arrows and En), and a third transgenic integration locus on chromosome 1 (thick arrow and Tg). At each locus of the three chromosomes, two sister chromatids gave a pair of identical hybridization signals. (C) RT-PCR analysis of α9 AChR endogenous and fusion transcripts in nasal epithelia of wild-type (WT) and transgenic (Tg) mice. Identical amounts of RNA templates were used in each PCR reaction. Presence (+) and absence (−) of RT were used as controls for each RNA sample. Three pairs of primers [labeled as Myc-tag, α9, and Pax6 (Left)] were used for each RNA sample in 35-cycle PCR reactions. PCR products were analyzed in 10% acrylamide gels, and sizes of these products were indicated (Right). Primers used here were described in the text.