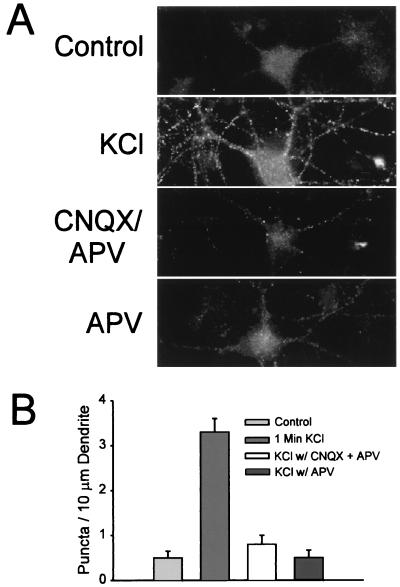
Figure 4.
Internalization of AMPARs induced by synaptically released glutamate. (A) Application of KCl (30 mM for 1 min) followed by 14 min chase incubation in normal medium caused significant internalization of AMPARs (compare top two panels). Blockade of glutamate receptors with CNQX and d-APV strongly inhibited this process, confirming that KCl-induced internalization of AMPARs is mediated by endogenously released glutamate binding to receptors. AMPAR internalization induced by KCl was also strongly inhibited by the NMDAR-specific antagonist d-APV. (B) Quantitation of AMPAR internalization in the absence and presence of receptor antagonists (n = 23 for each group).