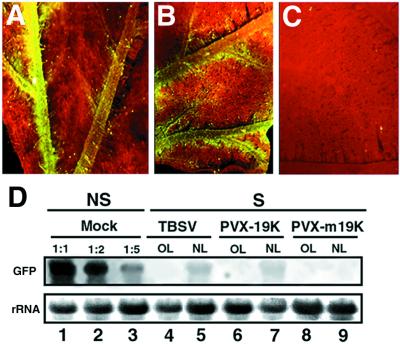
Figure 2.
Vein-specific suppression of PTGS caused by TBSV and PVX-19K. (A) Close-up image of a TBSV-infected leaf from a GFP-silenced N. benthamiana. (B) Close-up image of a PVX-19K-infected leaf from a GFP-silenced N. benthamiana. (C) Close-up image of a PVX-m19K-infected leaf from a GFP-silenced N. benthamiana. Photographs A, B, and C were taken under UV illumination from a dissecting microscope at 20 DPI. (D) Northern blot analysis of RNA extracted at 20 DPI from silenced (S) N. benthamiana infected with PVX-19K or PVX-m19K. RNA samples were taken either from old leaves (OL) or from new emerging leaves (NL). Equal amounts of each RNA sample (15 μg) were assayed by RNA gel blotting by using a 32P-labeled GFP cDNA as probe. Lanes 1–3 show a dilution series of GFP RNAs from a nonsilenced (NS) plant into total RNA from a nontransformed (NT) plant. GFP RNA was diluted to a one-half (1:2) or to one-fifth (1:5) of the reference sample (1:1). Ethidium bromide staining of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) shows equal loading of the samples.