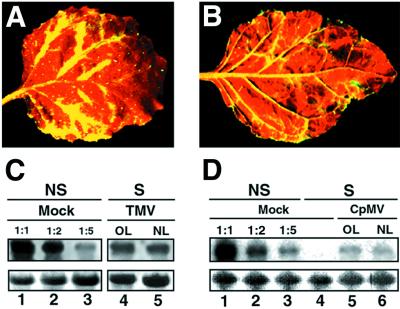
Figure 3.
Suppression of PTGS caused by TMV and CPMV occurs preferentially in the vicinity of the veins. (A) Close-up image of a TMV-infected leaf from a GFP-silenced N. benthamiana. (B) Close-up image of a CPMV-infected leaf from a GFP-silenced N. benthamiana. Photographs A and B were taken under UV illumination from a hand-held lamp at 20 DPI. (C) Northern blot analysis of RNA extracted at 20 DPI from silenced (S) N. benthamiana infected with TMV. RNA samples were taken either from old leaves (OL) or from new emerging leaves (NL). Equal amounts of each RNA sample (15 μg) were assayed by RNA gel blotting by using a 32P-labeled GFP cDNA as probe. Samples were separated on the same agarose gel and blotted on the same filter that was used in Fig. 2, thus allowing the use of the same GFP RNA dilution series as a reference. (D) Northern blot analysis of RNA extracted at 20 DPI from silenced (S) N. benthamiana infected with CPMV. Equal amounts of each RNA sample (15 μg) were assayed by RNA gel blotting by using a 32P-labeled GFP cDNA as probe. Mock control lanes 1–3 were prepared as in Fig. 2. Ethidium bromide staining of ribosomal RNA at the bottom shows equal loading of the samples.