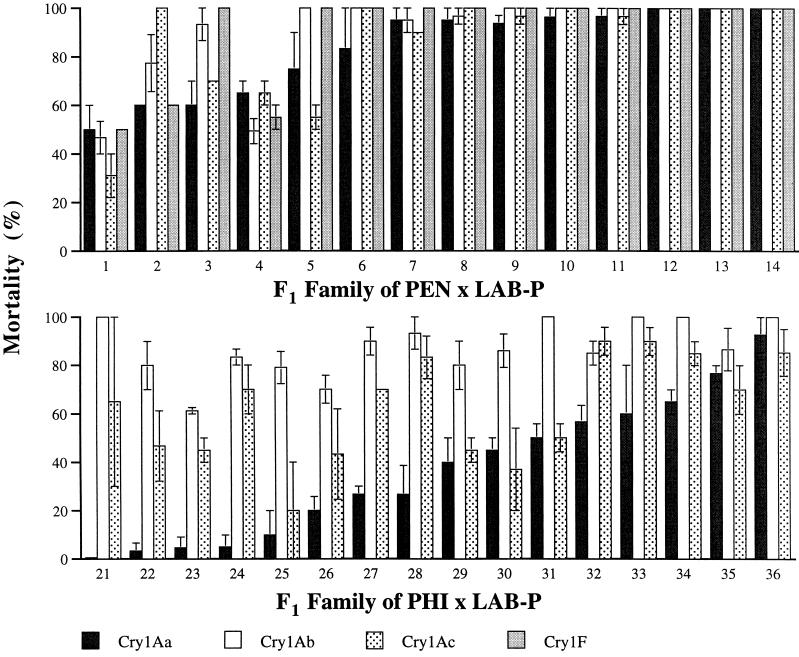
Figure 1.
Responses to Bt toxins from split broods of hybrid F1 progeny from single-pair crosses between strains of diamondback moth. (Upper) Resistant strain PEN × susceptible strain LAB-P (n = 1,605 larvae). (Lower) Resistant strain PHI × LAB-P (n = 1,451 larvae). Families are numbered from lowest (left) to highest mortality caused by Cry1Aa. Two or three groups of 9–11 larvae from each family were tested against each toxin (n = 59–121 larvae per family). Concentrations were 10 mg Cry1A toxin per liter and 10 ml formulated Cry1F per liter. Bars show mean mortality ± 1 SE. Genetic correlations were estimated from arcsine-transformed mortality data as described previously (14). Two-way ANOVA of the arcsine-transformed mortality data revealed significant effects of family (P < 0.0001 for both PEN and PHI), toxin (P = 0.0011 for PEN and P < 0.0001 for PHI), and family-by-toxin interaction (P < 0.0001 for PEN and P = 0.0002 for PHI).