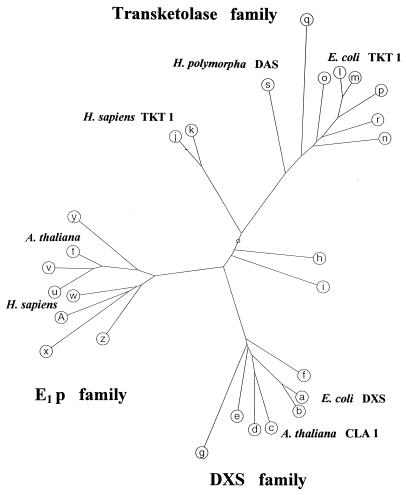
Figure 5.
Unrooted tree of DXP synthases (DXS family), transketolases, E1 proteins, and related proteins. A multiple alignment of sequences was constructed by a computer program (PepPepSearch) with an algorithm of Smith and Waterman (28). The alignment was obtained by using a deletion scoring function (29) and a Dayhoff matrix (30). The tree was generated by using an algorithm of Gonnet (31). Swiss-Prot/GenBank accession numbers of sequences are given for further identification. Characters a–g indicate DXS family sequences (a = E. coli U82664; b = Haemophilus influenzae P45205; c = A. thaliana U27099; d = Rhodobacter capsulatus P26242; e = Synechocystis sp. D90903; f = Bacillus subtilis P54523; g = Mycobacterium leprae P46708), h and i are sequences of unknown function consisting of 316 amino acid residues (Methanococcus jannaschii G64384) and 345 residues (Rhizobium sp. P55573). The transketolase family consists of j and k representing two human transketolases (P29401 and P51854), l = E. coli transketolase 1, P27302; m = H. influenzae P43757; n = Saccharomyces cerevisiae P23254; o = B. subtilis P45694; p = Alcaligenes eutrophus P21725; q = Mycoplasma genitalium P47312; r = Solanum tuberosum S58083, and s is dihydroxyacetone synthase (DAS, formaldehyde transketolase) from Hansenula polymorpha P06834. The E1 p family consists of E1 protein sequences from PHDCs (t = A. thaliana P52901; u = human M24848; v = S. cerevisiae P32473; w = B. subtilis P21881; x = Mycoplasma capricolum MCU62057; y = Thiobacillus ferrooxidans TFU81808) and E1 proteins of oxoisovalerate dehydrogenase complexes (z = B. subtilis P37941; A = Pseudomonas putida P09061.