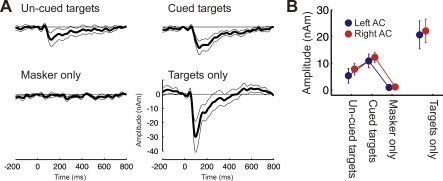
Figure 3. Experiment 1C: Cued Targets.
In this experiment, listeners attended passively to the stimulation. Targets started either after the informational masker (uncued targets) or two tones before the informational masker (cued targets). Except for the cue, the masker and targets used in the two conditions were identical. This setting was chosen to test the influence of perception on the ARN without the necessity for an active task by the listener. Listeners were naive as to the experiment's objective.
(A) Average source waveforms across listeners (n = 12) and hemispheres. Confidence intervals represent bootstrap-based t-intervals (two-tailed, p < 0.05).
(B) Mean amplitudes and standard errors of the mean in the time window from 75–175 ms post target tone onset. The ARN evoked by cued targets is significantly stronger than the ARN elicited by uncued targets.