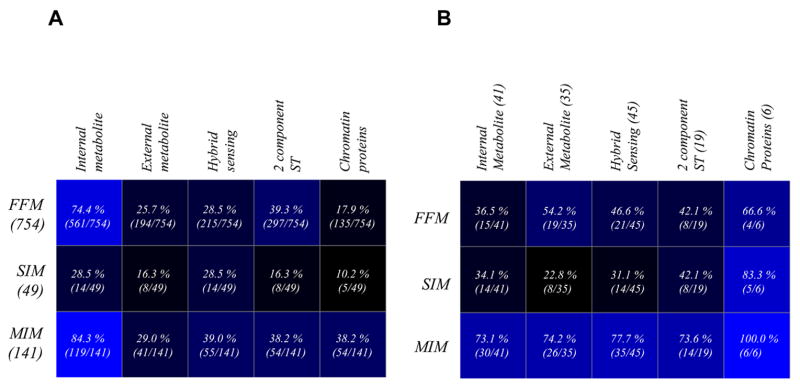
Fig 4.
Motifs and the types of signal sensed by TFs. Matrix plots showing the extent of prevalence of TFs from different types of signal-sensing modes in various types of motifs. The values in various boxes in the matrix on the left (A) are observed values normalized by the total number of motifs of that particular type found in the TRN. The corresponding boxes in the matrix on the right (B), however, contain observed values that are normalized by the total number of TFs in that particular type of signal sensing group in the TRN. The dark and light blue boxes respectively denote low and high extent of representation. Among the major groups of signal sensing TFs, external 2-component TFs display a higher tendency to occur in all three types of motifs, while internal signal sensing TFs and TFs sensing externally transported metabolites are preferentially found in FFMs and MIMs, respectively.