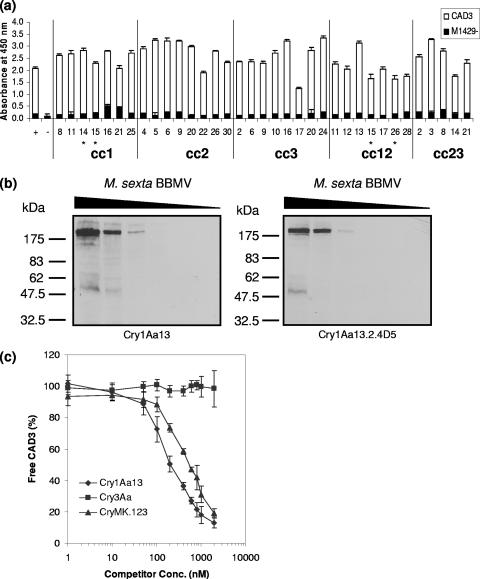
FIG. 9.
Cry toxin receptor binding. (a) Crybody binding to the cadherin receptors CAD3 and M1429−, as determined by ELISA. Solubilized Crybodies, Cry1Aa13 (+), and a control without toxin (−) were used to coat the wells of microtiter plates. Wells were probed with CAD3, M1429−, or buffer alone and bound receptor detected with Ni-nitrilotriacetic acid horseradish peroxidase. Absorbance values were corrected by subtracting the absorbance of corresponding controls incubated without receptors. The means and standard deviations of the results from four replicates are shown. Asterisks indicate Crybodies with mutations in the toxin framework. (b) Analysis of Cry1Aa13 and Cry1Aa13.2.4D5 binding to M. sexta BBMV receptors by ligand blot assay. On duplicate gels, 230, 46, 9.2, 1.8, 0.37, or 0.070 μg of total BBMV protein was resolved by SDS-PAGE and then electrotransferred to nitrocellulose membranes. The blots were then blocked and probed with either activated Cry1Aa13 or Cry1Aa13.2.4D5. Toxin binding was detected by incubation with anti-Cry1Aa polyclonal antibodies followed by anti-rabbit IgG antibodies conjugated to horseradish peroxidase. (c) Analysis of Cry1Aa13, CryMK.123, and Cry3Aa binding to CAD3. Various concentrations of Cry1Aa13, CryMK.123, and Cry3Aa were mixed with a constant amount of CAD3 (4 nM) and allowed to reach equilibrium. A portion of each sample was then transferred to an ELISA plate previously coated with Cry1Aa13, and the amount of free CAD3 was detected as described for panel a. The means and standard deviations of the results from three independent experiments are shown.