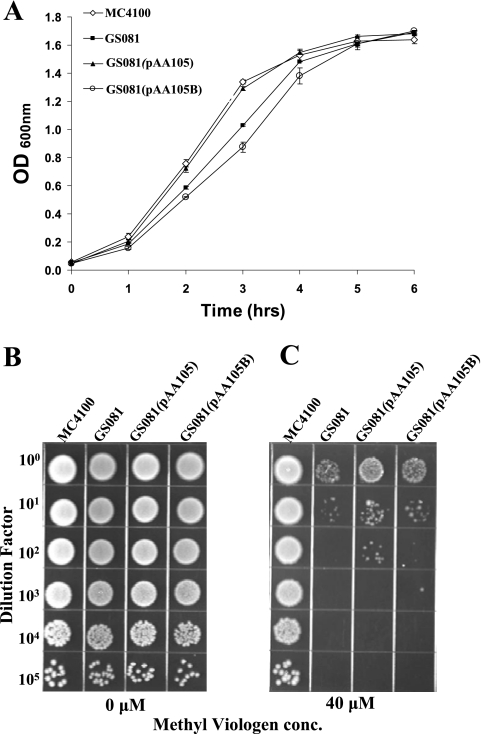
FIG. 9.
Complementation of an E. coli hfq mutant with the M. catarrhalis Hfq protein. (A) Growth curves of wild-type, mutant, and recombinant E. coli strains. The wild-type strain MC4100 (⋄), the hfq mutant GS081 (▪), the hfq mutant with the M. catarrhalis hfq gene provided in trans [GS081(pAA105)] (▴), and the hfq mutant containing the negative control plasmid [GS081(pAA105B)] (○) were suspended in LB broth to an OD600 of 1.0 and then diluted 1:20. These cultures were allowed to grow with aeration at 37°C, and the growth was monitored by measuring the absorbance at 600 nm every hour. (B and C) Cells of the wild-type, mutant, and recombinant E. coli strains were suspended to the same OD600 and then serially diluted and spotted onto BHI agar (B) and onto BHI agar containing 40 μM methyl viologen (C). The plates were dried and incubated overnight at 37°C.