FIG. 1.
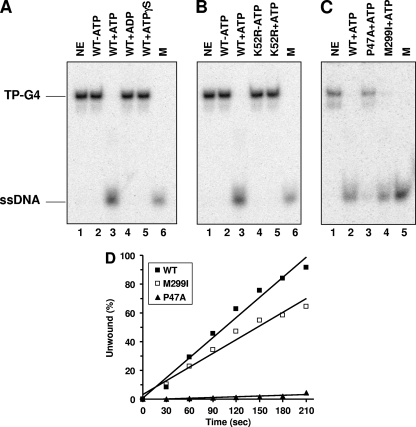
FANCJ efficiently unwinds G4 DNA in an ATP hydrolysis-dependent manner. (A) G4 unwinding assays were performed by incubating 4.8 nM wild-type (WT) FANCJ with 0.5 nM TP-G4 DNA substrate at 30°C for 15 min under standard helicase assay conditions as described in Materials and Methods. Lane 1, no-enzyme control (NE); lanes 2 to 5, FANCJ G4 helicase reaction mixtures with or without the indicated nucleotide (2 mM); lane 6, 32P-labeled single-stranded oligonucleotide marker (M). (B) Catalytically inactive FANCJ mutant protein K52R fails to unwind G4 DNA. Lane 1, no-enzyme control; lanes 2 and 3, wild-type FANCJ (4.8 nM) in the absence or presence of 2 mM ATP; lanes 4 and 5, K52R (4.8 nM) in the absence or presence of 2 mM ATP; lane 6, marker. (C) Wild-type FANCJ (4.8 nM) or variant forms (with the mutation P47A or M299I; 4.8 nM) tested for G4 unwinding in the presence of 2 mM ATP. Lane 1, no-enzyme control; lane 2, wild-type FANCJ; lane 3, FANCJ P47A mutant protein (P47A); lane 4, FANCJ M299I mutant protein (M299I); lane 5, marker. (D) Kinetic analyses of DNA unwinding of the G4-TP substrate by wild-type FANCJ or FANCJ polymorphic variants. Wild-type FANCJ (0.3 nM) or an associated variant (FANCJ M299I or P47A mutant protein) was incubated with the 0.5 nM TP-G4 DNA substrate under standard helicase reaction conditions at 30°C for the indicated times. A quantitative analysis of results from FANCJ helicase assays is shown.