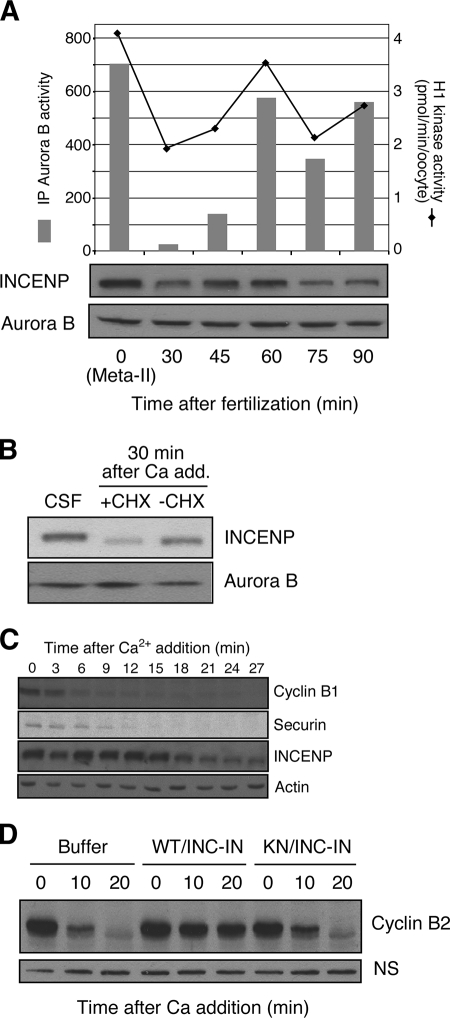
FIG. 4.
Aurora B inactivation at fertilization. (A) Oscillation of Aurora B kinase activity. Newly fertilized eggs were homogenized at the indicated time points and immunoblotted with anti-INCENP and anti-Aurora B antibodies (lower panel). Aurora B kinase activity was measured with immunoprecipitated (IP) Aurora B by using histone H3 as a substrate, and total histone H1 kinase activity in the extract was assayed as described in Materials and Methods. (B) INCENP is degraded at fertilization. Xenopus CSF extracts, arrested at meta-II, were first supplemented with cycloheximide (+CHX) or water (−CHX), released from CSF arrest by the addition (add.) of CaCl to 0.8 mM, and finally incubated for 30 min. The equivalent of 0.5 μl of extract was immunoblotted with anti-INCENP or anti-Aurora B antibodies. (C) Kinetics of INCENP degradation. Extracts were prepared from meta-II, CSF-arrested eggs. Five microliters of radiolabeled securin in reticulocyte lysate was added to 100 μl of CSF extract. Calcium was added to initiate CSF release, and cycloheximide was added to block new protein synthesis. Western blotting was performed at the indicated times by using antibodies to cyclin B1, INCENP, or actin (loading control) as indicated. The degradation of securin was monitored by autoradiography. (D) Active Aurora B-INCENP blocks CSF release. Xenopus CSF-arrested egg extracts were supplemented with bacterially expressed recombinant wild-type Aurora B-INCENP-IN (WT/INC-IN) complex or the kinase-dead (KN) Aurora B-INCENP-IN complex; after 10 min at room temperature, anaphase and cyclin B proteolysis were initiated by further supplementation with 0.8 mM CaCl2. At the indicated times, 0.5 μl of each extract was assessed for the level of cyclin B2 by Western blotting. A nonspecific band (NS) recognized by the anti-cyclin B1 antibody served as a loading control.