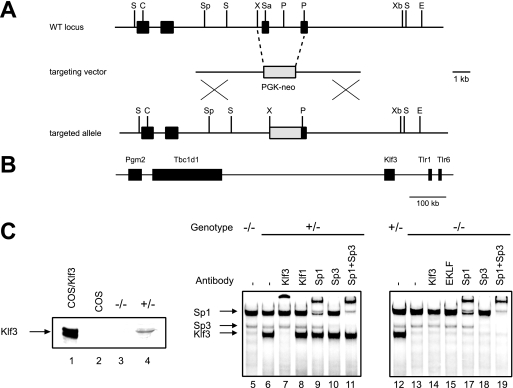
FIG. 1.
Targeted disruption of Klf3 in mice. (A) Generation of Klf3 knockout mice. Schematic representation of the wild-type (WT) Klf3 locus (with a partial restriction map), the targeting vector, and the targeted allele. Black boxes represent exons. The zinc finger domain is contained in the last two exons. The gray box represents the phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK)-neo cassette. Abbreviations: S, StuI; C, ClaI; Sp, SpeI; X, XhoI; Sa, SalI; P, PmlI; Xb, XbaI. (B) Schematic showing genomic location of murine Klf3 and neighboring genes on chromosome 5. Pgm2, glucose phosphomutase 2; Tbc1d1, TBC1 domain family, member 1; Tlr1, Toll-like receptor 1; and Tlr6, Toll-like receptor 6. (C) Western blotting (left panel) using anti-Klf3 serum, showing full-length Klf3 ectopically expressed in COS cells (lane 1), COS cells alone (lane 2), and spleen samples from Klf3 knockout and heterozygous littermates (lanes 3 and 4, respectively). The right panels (lanes 5 to 18) show EMSAs using the β-major globin gene promoter −90 CACCC box. The bands generated by Klf3, Sp1, and Sp3 are indicated by arrows and are supershifted by appropriate antisera.