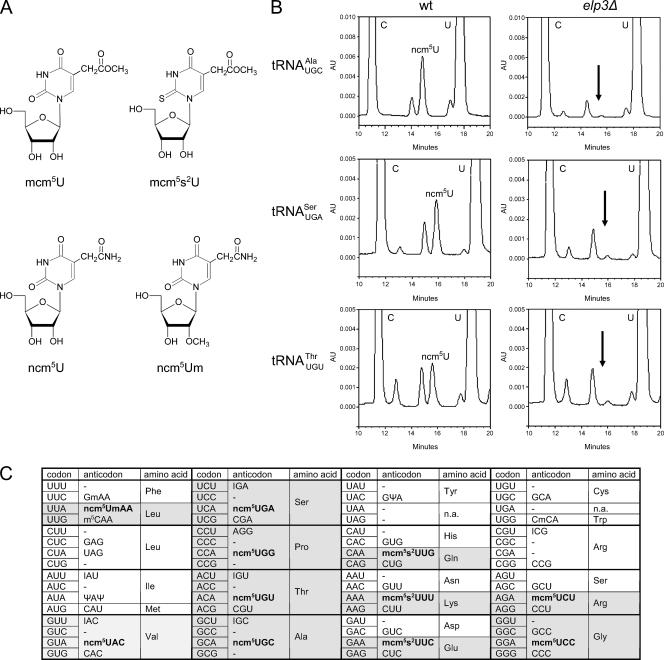
FIG. 1.
Eleven S. cerevisiae tRNA species contain an xm5U derivative at the wobble position. (A) Structures of mcm5U, mcm5s2U, ncm5U, and ncm5Um. (B) The indicated tRNA species was isolated from either wild-type (UMY2893) or elp3Δ (UMY2916) cells, and their nucleoside compositions were analyzed by HPLC. The part of the chromatogram between 10 and 20 min is shown in each case. The arrow indicates expected retention time of ncm5U (right panels). The small peak at this position represents an unrelated compound with an UV absorption spectrum different from that of ncm5U. (C) The genetic code and distribution of cytoplasmic S. cerevisiae tRNAs. The anticodon sequences of the 42 different tRNA species (1 initiator and 41 elongator tRNAs) are indicated (21, 25, 32, 39). For anticodons with an uncharacterized RNA sequence, the primary sequence is shown. The initiator and elongator tRNAMet species have identical anticodon sequences. The wobble rules suggest that an inosine (I34) residue allows paring with U, C, and sometimes A. A tRNA with a G or its 2′-O-methyl derivative (Gm) at the wobble position should read U- and C-ending codons. Presence of a C34 residue or its 5-methyl (m5C) or 2′-O-methyl (Cm) variant should only allow pairing with G. The pseudouridine (Ψ)-containing tRNAIle is presumably unable to pair with the methionine AUG codon. The anticodons containing an xm5U derivative are shown in bold. In tRNAA66Pro, the A34 residue is most likely modified to I34 (see text). AU, absorbance units; wt, wild type.