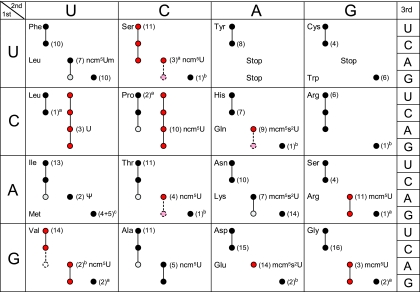
FIG. 7.
The genetic code and decoding abilities of individual tRNA species. Codons read by a tRNA are indicated by circles and connecting lines. Red and pink circles represent tRNA species for which the decoding properties were investigated in this article. Pink circles connected with a dashed line indicate that the tRNA species reads the codon only when it is overexpressed. The empty dashed circle for tRNAIACValis shown only to indicate that this inosine-containing tRNA species does not efficiently read the GUA codon. The nucleoside at the wobble position is given for the 13 wobble uridine-containing tRNA species. Black and gray circles represent decoding abilities predicted by the wobble hypothesis, the revised wobble rules, and the distribution of tRNA species. A gray circle indicates that the tRNA species is less likely to read the codon. The number of genes coding for a tRNA species is indicated next to the circle for the complementary codon. The following qualifications apply: a superscript a indicates that the gene(s) encoding the tRNA is nonessential; a superscript b indicates that the gene(s) encoding the tRNA is essential; where two values are given (superscript c) four genes code for tRNAiMet, and five code for tRNAmMet.