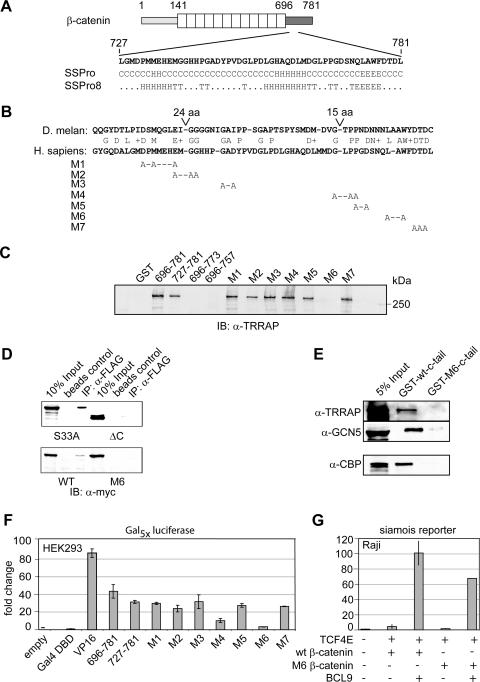
FIG. 6.
Mutational analysis of the β-catenin C terminus identifies residues that are important for coactivator binding and transactivation. (A) The C terminus (aa 727 to 781) of β-catenin is predicted to consist of helical (H) and β-sheet (E) motifs (T, turn; C, unstructured). Secondary structure contribution was calculated from the primary amino acid sequence (16). (B) Comparison of armadillo and β-catenin reveals conserved amino acids. Combinations of these amino acids were mutated to alanine as indicated. (C) L774A/W776A (M6) mutation of the β-catenin C terminus abolishes in vitro TRRAP binding. Mutant constructs were fused to GST and examined for binding to TRRAP in a GST pulldown assay with HeLa nuclear extract. Bound and subsequently eluted TRRAP was detected by immunoblot analysis (IB) with an anti-TRRAP (α-TRRAP) antibody. (D) L774A/W776A (M6) β-catenin displays reduced TRRAP binding in the context of the full-length protein. myc-tagged β-catenin constructs and Flag-TRRAP were transiently expressed in HEK293 cells and analyzed for interaction in coimmunoprecipitation assays. IP, immunoprecipitation; WT, wild type. (E) L774A/W776A (M6) β-catenin displays also reduced binding toward CBP. GST pulldown assays with wild-type and M6 mutant β-catenin C-terminal peptides were performed using Pd36 nuclear extract. (F) Transient transfections for determination of the transactivation potentials of various mutant β-catenin constructs that had been fused to the Gal4 DBD. The indicated gene constructs (0.1 μg) were transfected, together with a luciferase reporter carrying multimerized Gal4-binding sites, into HEK293 cells. (G) BCL9 (0.5 μg) activates the siamois reporter (1 μg) independently of the M6 β-catenin (3 μg) mutation in a transient transfection assay with Raji cells.