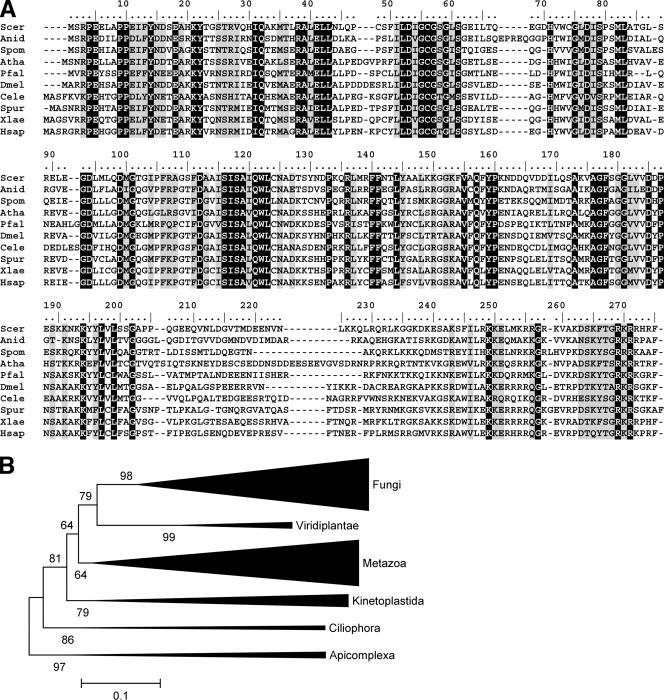
FIG. 4.
Bud23 is highly conserved but restricted to eukaryotes. (A) BLAST sequence alignment of Bud23 orthologs. Bud23 orthologs were from the following species (the accession numbersof these orthologs shown in brackets): Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Scer) [6319895], Aspergillus nidulans (Anid) [67539238], Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Spom) [19115061], Arabidopsis thaliana (Athal) [15242087], Plasmodium falciparum (Pfal) [124506365], Drosophila melanogaster (Dmel) [21355093], Caenorhabditis elegans (Cele) [17552330], Strongylocentrotus purpuratus (Spur) [72006191]), Xenopus laevis (Xlae) [148234441], and Homo sapiens (Hsap) [23199995]. Gaps introduced to maximize alignment are indicated by dashes. (B) Phylogenetic tree of Bud23 orthologs calculated using the neighbor-joining method as described in Materials and Methods. Lengths of branches correspond to the estimated evolutionary distances between Bud23 variants from different taxons (the bar below the tree indicates the distance of 0.1 unit according to the JTT matrix). Numbers at the nodes indicate the statistical support for grouping of the corresponding taxons, calculated from 1,000 bootstrap resamplings of the alignment. Values close to 100 indicate strong support.