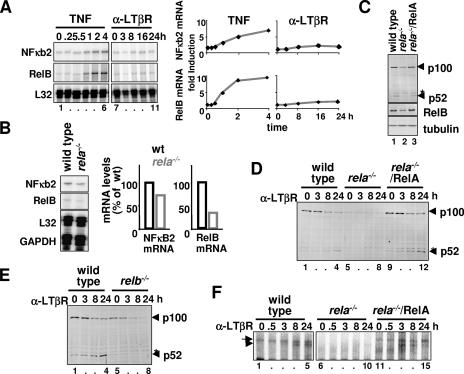
FIG. 2.
RelA is required for LTβR signaling and controls steady-state RelB expression. (A) RPA to examine NF-κB2 and RelB mRNA levels in wild-type MEFs stimulated with TNF or LTβR agonist (left panel). Relative induction levels of NF-κB2 and RelB mRNA in response to TNFR or LTβR stimulation are plotted after normalizing to L32 mRNA (right panel). (B) Steady-state level of NF-κB2 and RelB mRNA in wild-type or rela−/− MEFs was examined by RPA (left panel). Respective mRNA levels were quantified and normalized to L32 and GAPDH mRNA and plotted (right panel). (C) Immunoblotting for p100 and RelB in wild-type, rela−/−, or rela−/− MEFs reconstituted with a retroviral RelA transgene. Presence of a nonspecific band is denoted with an asterisk. (D and E) Immunoblotting to examine p100 processing into p52 during LTβR signaling in MEFs of the indicated genotypes. (F) NF-κB-DNA binding activities induced upon LTβR stimulation in rela−/− MEFs that express the RelA transgene were analyzed by EMSA. α, anti.