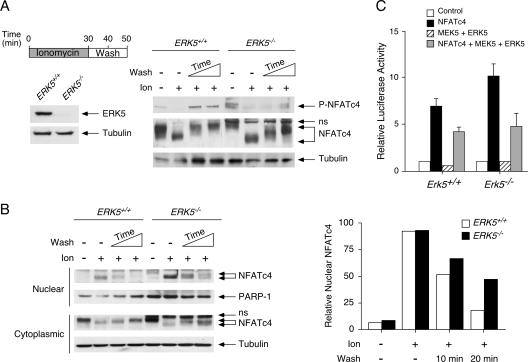
FIG. 6.
ERK5 regulates NFATc4 phosphorylation and nucleocytoplasmic shuttling. (A) Ablation of ERK5 affects electrophoretic mobility of NFATc4. Erk5+/+ and Erk5−/− MEFs were stimulated with ionomycin for 30 min before ionomycin withdrawal and then washed (10 or 20 min). Phosphorylation at Ser168,170 of endogenous NFATc4 was determined by phospho-NFATc4 monoclonal antibody (P-NFATc4). The electrophoretic mobility of NFATc4 was determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The expression of tubulin is also shown. The expression of ERK5 in Erk5+/+ and Erk5−/− MEFs is shown to confirm the genotype. (B) ERK5 regulates the nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of NFATc4. Erk5+/+ and Erk5−/− MEFs were stimulated with ionomycin for 30 min before ionomycin withdrawal and then washed (10 or 20 min). The amounts of NFATc4 in cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions were determined by immunoblotting analysis. The expression of tubulin and PARP-1 is shown. The relative intensity of nuclear NFATc4 (nucleocytoplasmic plus nuclear) was quantified by ImageQuant software and presented. The results are representative of three independent experiments. (C) ERK5 regulates NFATc4-mediated gene transcription. The Erk5+/+ or Erk5−/− MEFs were transiently transfected with an NFAT-luciferase reporter plasmid together with an expression vector for wild-type NFATc4. Cells were also cotransfected with MEK5 and ERK5 as indicated. Cells were harvested 36 h after transfection, and luciferase activity was normalized to β-galactosidase activity and presented (mean ± SD [n = 4]).