Figure 1.
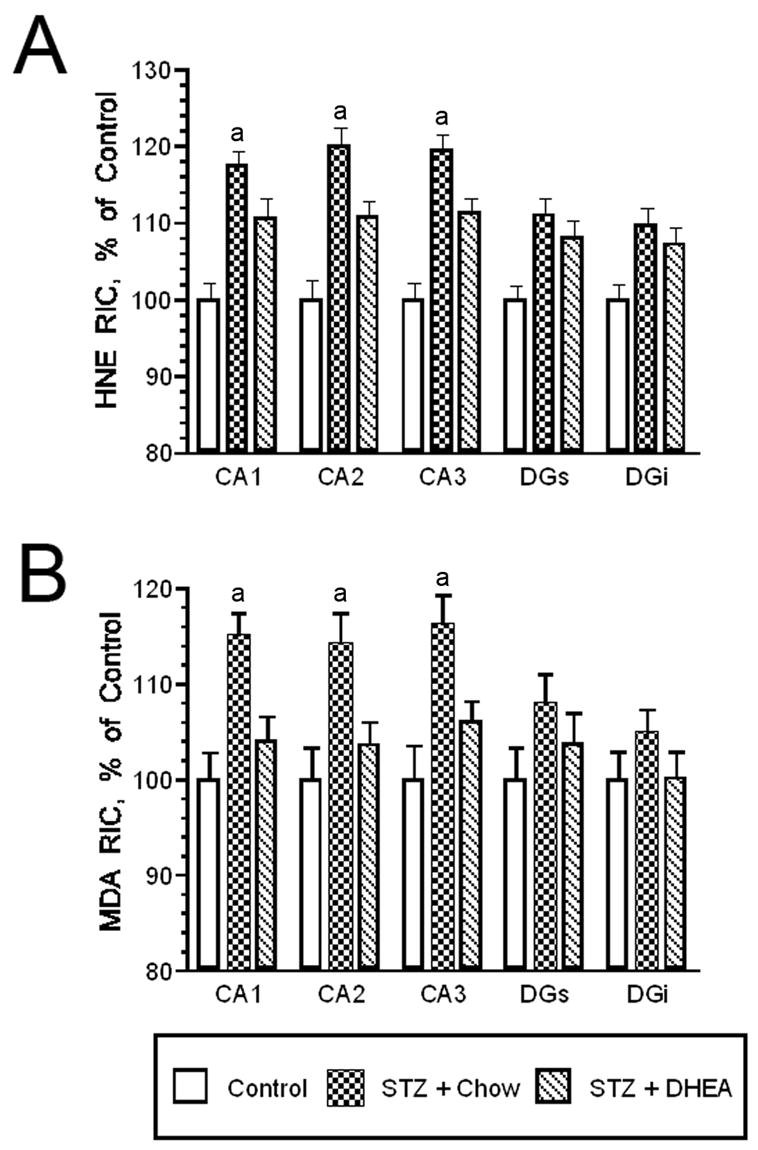
DHEA administration attenuates diabetes/stress mediated increases in oxidative stress. Streptozotocin diabetic rats subjected to chronic (i.e. 21 day) stress were provided access to normal chow or chow supplemented with 0.4% DHEA. Panel A. Radioimmunocytochemistry determined that diabetic rats subjected to stress provided normal chow exhibited the expected increases in HNE radioimmunolabeling the Ammon’s Horn of the hippocampus, increases that were significantly reduced in diabetic/stress rats provided the DHEA supplemented diet. Panel B. Similarly, the DHEA supplemented diet significantly reduced MDA radioimmunoreactive levels in Ammon’s Horn in diabetic rats subjected to chronic stress. See text for details. [a = P < 0.05]
