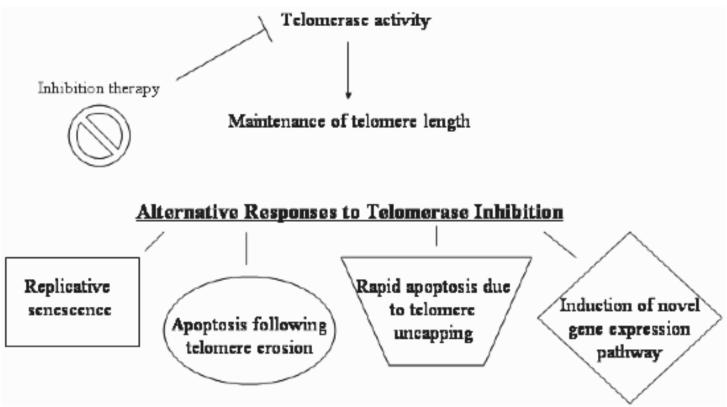
Fig. 2.
Diagram illustrating the possible outcomes of telomerase inhibition. Inhibition of telomerase prevents the maintenance of telomere length in telomerase-positive cells. As a result, telomerase may shorten, leading to eventual replicative senescence or apoptosis. Telomerase inhibition may also cause rapid cell death without telomere shortening and the induction of a novel gene expression pathway (discussed later in review).