Figure 8.
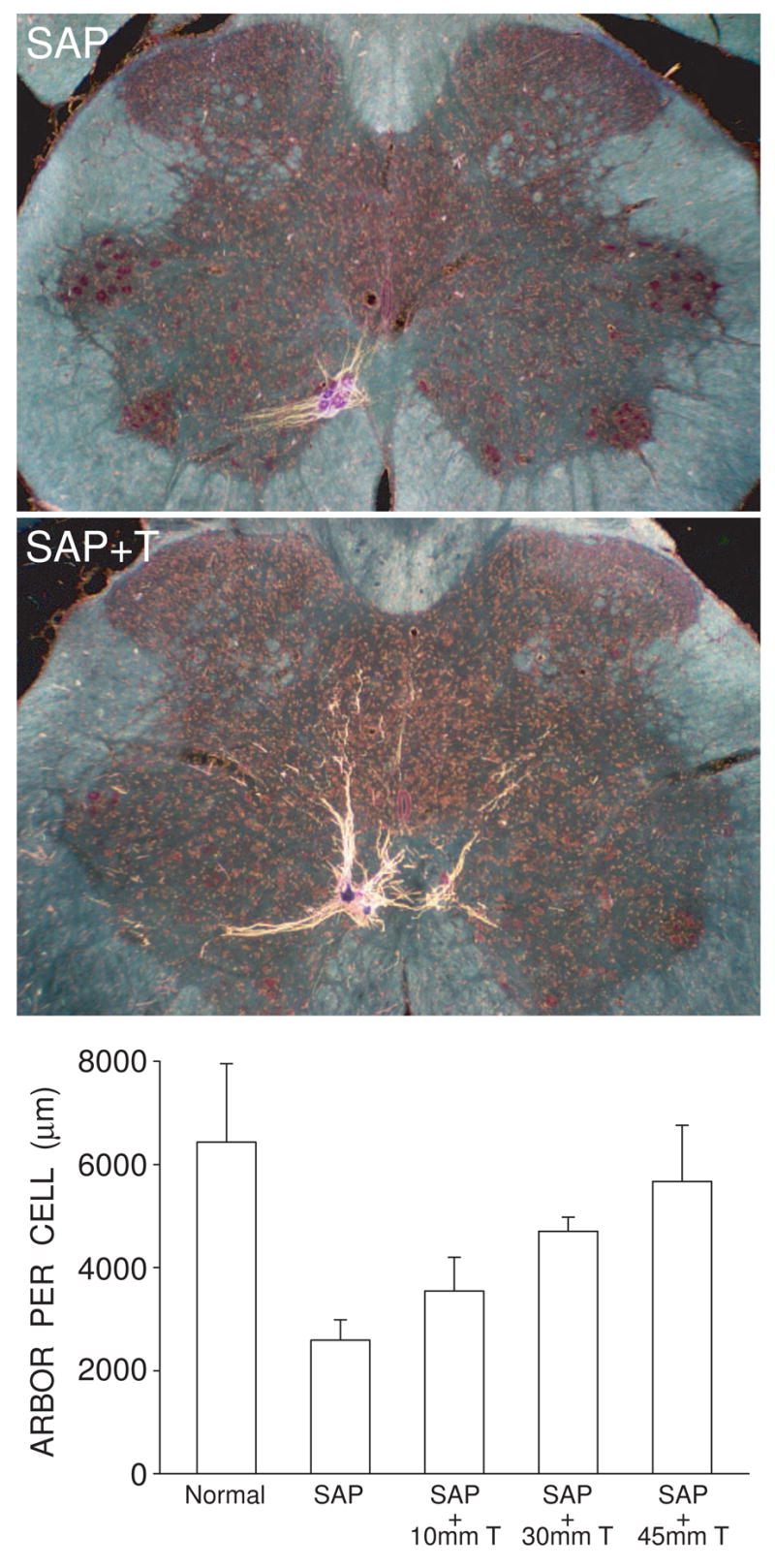
Testosterone treatment is neurotherapeutic in SNB motoneurons, attenuating induced dendritic atrophy resulting from the death of nearby motoneurons. (Left) Darkfield digital micrographs of transverse sections through the lumbar spinal cords of males whose SNB motoneurons have been partially depleted with the toxin saporin, and then left untreated (SAP) or given supplemental testosterone (SAP + T), after BHRP injection into the left BC muscle. (Right) SNB dendritic lengths expressed as length of arbor per labeled motoneuron for normal males and saporin-treated males with or without supplemental testosterone. Partial motoneuron depletion reduces the dendritic arbor of remaining motoneurons. However, in rats whose androgen levels had been supplemented with varying levels of T, this atrophy is attenuated in a dose-dependent manner. Bar heights represent means ± SEM. (Data from Coons et al., 2007.)
