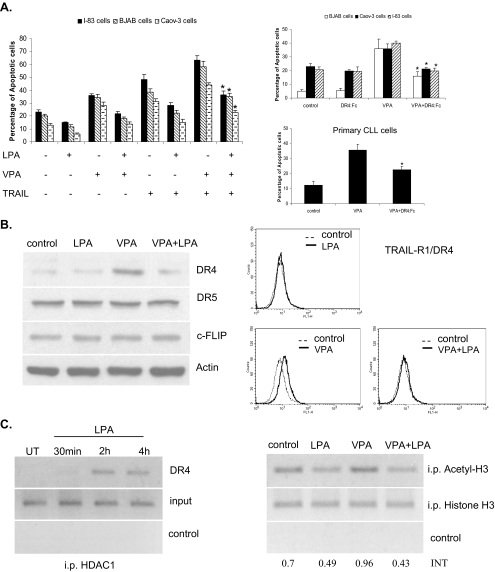
FIGURE 2.
LPA prevents the HDIs and TRAIL-induced apoptosis via the death receptor suppression through HDAC1 binding to the promoter of DR4. A, BJAB, I-83, and CaOv-3 cells were treated with VPA (1 mm) and TRAIL (1 ng/ml) individually or in combination with LPA, as indicated, for 48 h. The percentages of apoptotic cells were determined by membrane permeability assay. Apoptotic cells were scored, with a total of 200 cells being counted for each condition. Standard error was determined on the basis of three independent experiments, and an asterisk represents significant difference (a p value of <0.005) between VPA + TRAIL-treated cells in the presence of LPA compared with the absence of LPA. BJAB, I-83, CaOv-3, and primary CLL cells were treated with VPA (1 mm). The cells were also incubated with DR4:Fc protein (100 ng/ml) as indicated. The amount of apoptosis was determined by membrane permeability assay. Error bars represent the standard errors for three independent experiments, and an asterisk represents a significant difference (p value of <0.005) between VPA-treated cells and VPA + DR4:Fc-treated cells. B, I-83 cells were treated with 1 mm VPA alone or in combination with LPA for 36 h. The protein levels of DR4, DR5, and c-FLIP were examined by Western blotting. The same treated cells were used to determine the cell surface expression of DR4 by flow cytometry. C, cells were treated with LPA (10 μm) over a time course and analyzed using the ChIP assay with anti-HDAC1 antibody. DNA was analyzed by PCR using primers specific for the DR4 promoter. Figure is representative of three separate experiments. Samples with no antibody added were used as a negative control, and total DNA was used as the input control, and the same ChIP experiments were carried out using acetyl-H3 and H3 antibodies, when the cells were treated with VPA alone or in combination with LPA.