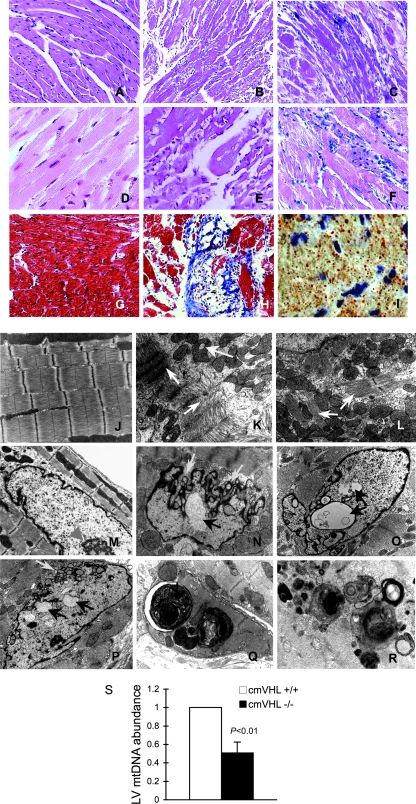
FIG. 2.
Absence of VHL from cardiac myocytes results in myocyte disassembly and loss, replacement fibrosis, automacrophagocytosis, lipid accumulation, organelle inclusions, and an altered nuclear envelope. (A to C) Hematoxylin and eosin staining (200× magnification) of myocardia from mice with cardiac myocyte-specific deletion of VHL (cmVHL−/−) reveals severe myocardial degeneration with thinning and loss of cardiac muscle bundles (B and C) compared to VHL+/+ control littermate hearts (A). Also visible is patchy infiltration by inflammatory cells (C). (D to F) Analysis at 400× magnification further demonstrates myocardial degeneration and nonuniformity of cardiac muscle bundles (E and F) and cellular infiltration (F) compared to control myocardium (D). (G and H) Myocyte loss and replacement fibrosis is also shown by Mason's trichrome staining of cmVHL−/− hearts (H) versus control littermates (G). (I) cmVHL−/− hearts also accumulate lipids, as shown by oil red O staining. (J to L) Ultrastructural analysis by transmission EM demonstrates disarray and disassembly of myofibrils (white arrows), irregular spacing of Z-bands, irregular orientation of myofibrils, and mitochondrial inclusions (yellow arrow) in cmVHL−/− hearts (K and L) versus the normal architecture of control hearts (J). (N to P) Nuclei from cmVHL−/− hearts exhibit irregular nuclear morphology with prominent folding and blebbing of the nuclear envelope (blue arrows) and multiple nuclear inclusions (black arrows) compared to the normal nuclear architecture in control myocardium (M; arrowhead indicates nucleolus). (Q and R) Multilaminar vesicles (autophagosomes) containing whole organelles (e.g., mitochondria), myofibrils, and other cellular debris were seen frequently in cmVHL−/− hearts, indicating increased autophagy/macroautophagy. (S) Quantitative PCR for mitochondrial DNA revealed a decrease in cmVHL−/− hearts (n = 5 per genotype). For ultrastructural and histological analysis, ≥5 hearts per genotype were studied, with at least five sections and five separate fields/section evaluated per heart.