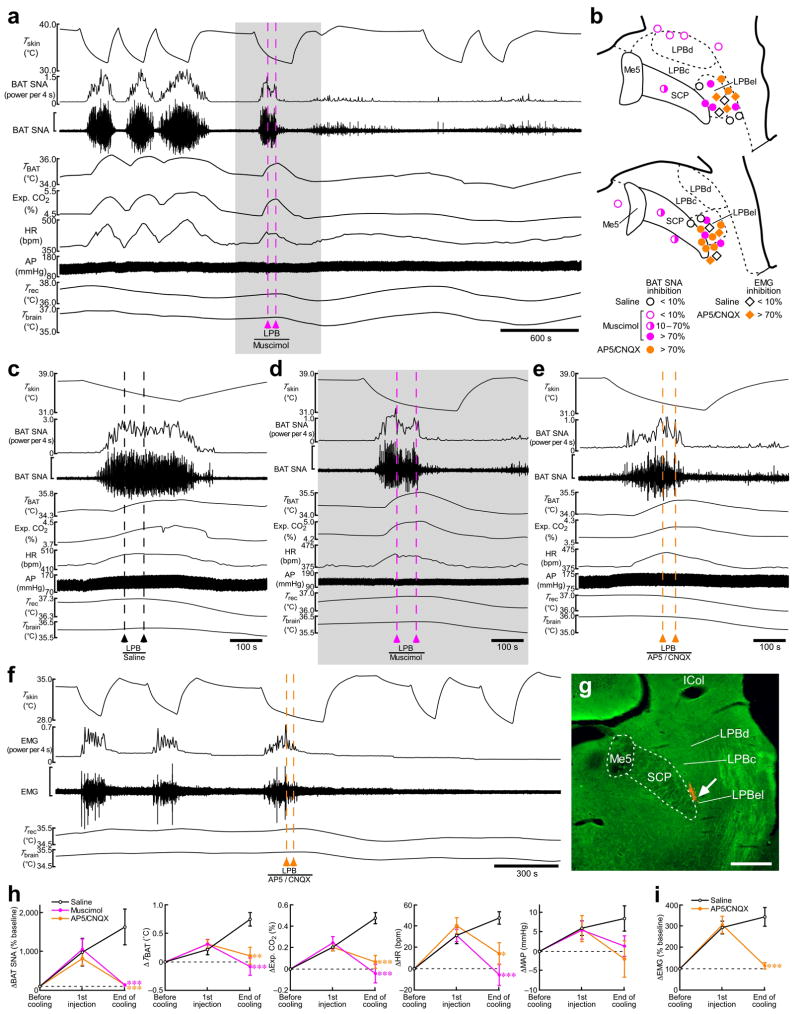
Figure 3.
Inhibition of neuronal activity or blockade of ionotropic glutamate receptors in the LPB reverses skin cooling-evoked thermogenic, metabolic and cardiac responses. (a) Skin cooling-evoked changes in BAT SNA, BAT temperature (TBAT), expired (Exp.) CO2, heart rate (HR), arterial pressure (AP), Trec, and Tbrain before and after bilateral nanoinjections of muscimol into the LPB (pink dashed lines). The gray area is expanded in d. The vertical scale bar for the BAT SNA trace represents 100 μV. (b) Composite drawing of sites of saline, muscimol (2 mM) or AP5/CNQX (5 mM each) nanoinjections (60 nl) in and around the LPB with their inhibitory effects on the skin cooling-evoked increase in BAT SNA or EMG. The right side of the symmetric bilateral injections is shown. (c–e) Effect of bilateral nanoinjections of saline (c), muscimol (d) and AP5/CNQX (e) into the LPB on skin cooling-evoked changes in physiological variables. The vertical scale bar for the BAT SNA trace represents 200 μV (c), 100 μV (d) and 50 μV (e). (f) Skin cooling-evoked changes in EMG before and after bilateral nanoinjections of AP5/CNQX into the LPB (orange dashed lines). The vertical scale bar for the EMG trace represents 400 μV. g, Representative view of a nanoinjection site in the LPBel as identified with a cluster of fluorescent beads (arrow). Scale bar, 0.5 mm. (h,i) Group data (mean ± s.e.m.) showing the effect of saline (n = 5), muscimol (n = 7) or AP5/CNQX (n = 8) nanoinjections into the LPBel on skin cooling-evoked changes in BAT SNA, TBAT, Exp. CO2, HR and MAP (h) and the effect of saline (n = 4) and AP5/CNQX (n = 5) nanoinjections into the LPBel on skin cooling-evoked changes in EMG (i) (see c–f). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, compared with the saline-injected group (Bonferroni post hoc test following a one-way factorial ANOVA).