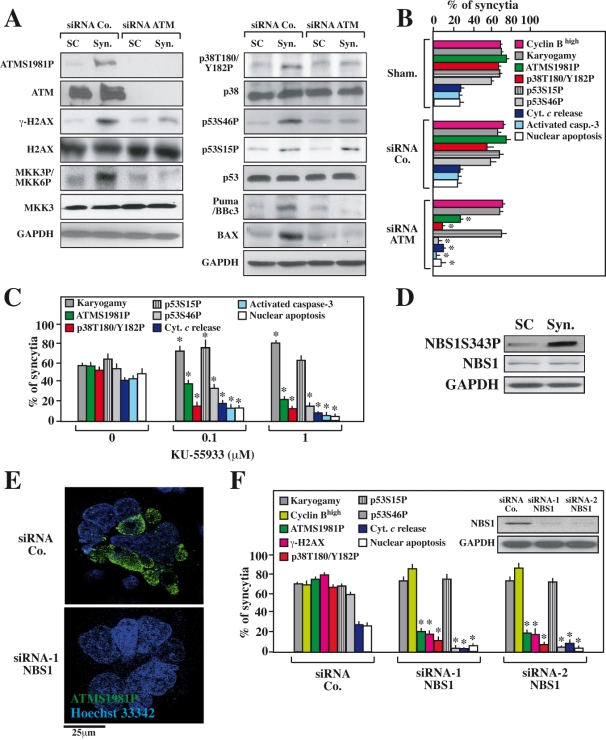
Figure 3. Effect of the ATM knockdown or pharmacological ATM inhibition on the Env-elicited apoptotic signal transduction cascade.
HeLa CD4 and HeLa Env cells were separately transfected with the indicated siRNAs and 36 h later the cells were cocultured for further 36 h, followed by the immunoblot detection of the indicated proteins and phoshoproteins (A) or, alternatively, by immunofluorescence detection (B, C) of the indicated parameters (X±SD, n = 5). Alternatively, the cells were not transfected and rather treated with the chemical ATM inhibitor KU-55933 (C), at a dose that did not inhibit karyogamy (100 nM or 1 µM), followed by the determination of the indicated parameters by immunofluorescence analyses (X±SD, n = 3). Moreover, the two cell lines (HeLa CD4 and HeLa Env) were both transfected with a control siRNA or two distinct siRNAs targeting NBS1 (D,E), followed by immunoblot detection of NBS1 after admixture at a 1∶1 ratio (D) or coculture for 36 h and determination of the indicated parameters by immunofluorescence (E, F). Representative fluorescence microphotographs are shown in E and quantitative data (X±SD, n = 3) are summarized in F. Asterisks mark significant inhibitory effects of the ATM-specific siRNA (as compared to a control siRNA in B), of KU-55933 (as compared to untreated cells in C) or of the two NBS1-specific siRNAs (as compared to a control siRNA in F).