Fig. 3.
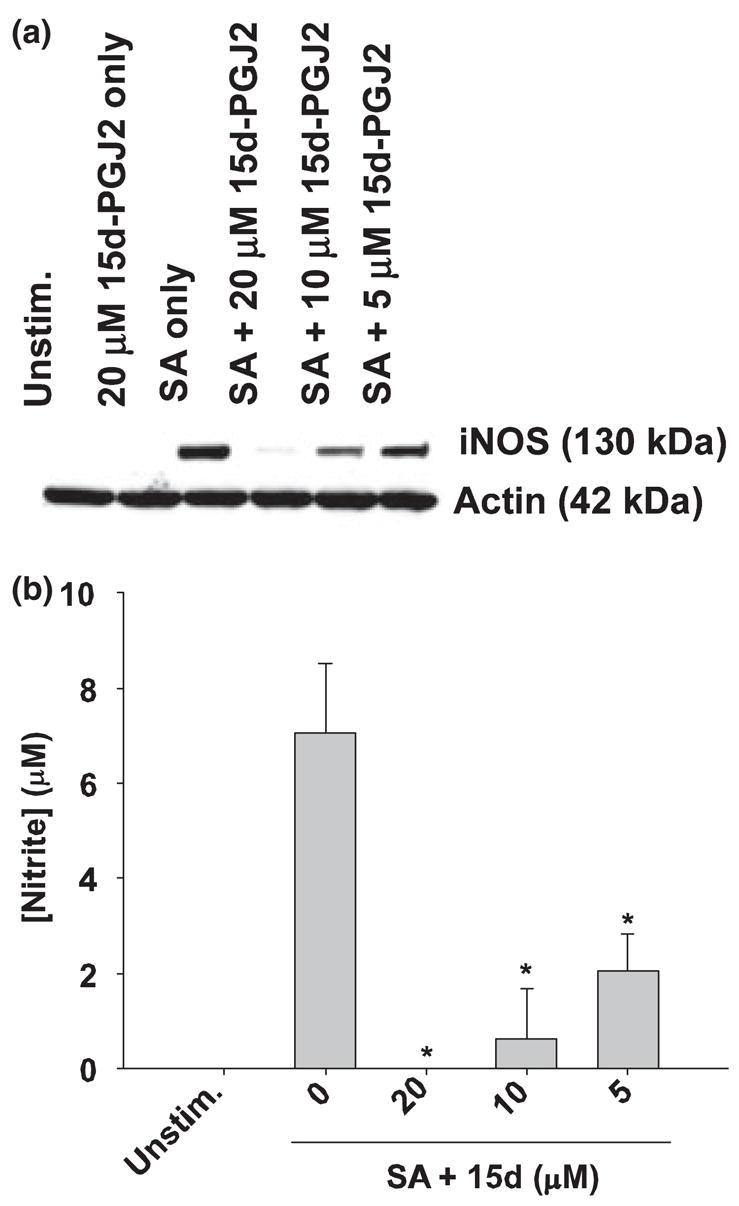
15d-PGJ2 inhibits iNOS protein expression and subsequent NO production in S. aureus-stimulated astrocytes. Astrocytes were seeded in 6-well plates at 1 × 106 cells per well. After an overnight incubation, cells were pre-treated with 20 μM of 15d-PGJ2 only, or various concentrations of 15d-PGJ2 for 1 h prior to stimulation with 108 cfu S. aureus (SA). In (a), Western blots were performed on astrocyte protein extracts (40 μg total protein) collected at 24 h following S. aureus stimulation as described in Materials and methods. Following transfer, membranes were probed with an iNOS-specific antibody and subsequently stripped and re-probed for β-actin to verify uniformity in gel loading. In (b), cell-free supernatants were analyzed for nitrite production (presented in μM). Results are reported as the mean ± SD of three independent wells for each experimental treatment. Significant differences between astrocytes treated with S. aureus versus cells exposed to the various concentrations of 15d-PGJ2 + S. aureus are denoted with asterisks (*p < 0.05). Results are representative of five independent experiments.
