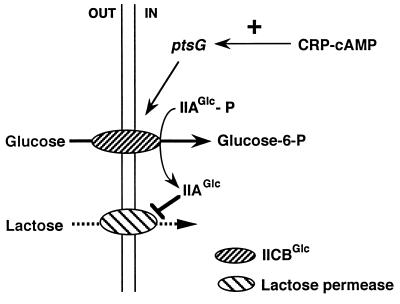
Figure 6.
A model explaining the role of CRP–cAMP in the glucose effect in the glucose–lactose system. The transport and phosphorylation of glucose by glucose PTS (IIAGlc + IICBGlc) increase the dephosphorylated IIAGlc that prevents the uptake of lactose by inhibiting the lac permease activity. An important role of CRP–cAMP in the glucose effect is to support inducer exclusion by activating the ptsG transcription. The reduction in ptsG transcription is responsible for the failure of the glucose effect in the absence of CRP–cAMP.