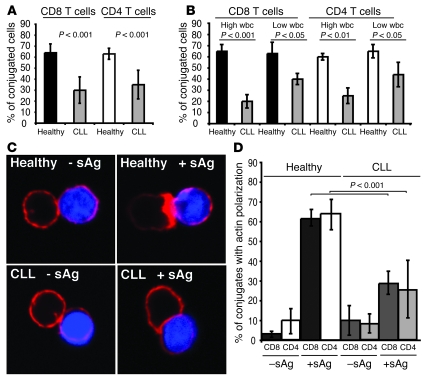
Figure 1. CLL patients have impaired T cell immune synapse formation.
(A) T cell conjugates formed between T cells from CLL patients or age-matched healthy donors and sAg-pulsed autologous CLL B cells or healthy B cells, respectively, were scored by visual counting using a confocal microscope. Each data set shows the mean ± SD from 6 independent experiments, with 50 random T cells analyzed per experiment. (B) Autologous conjugate experiments were performed as in A, comparing CLL patients with low (less than 20 mm3) absolute wbc versus high wbc (20 mm3 or more) with age-matched healthy donor cell conjugates. Each data set shows the mean ± SD from 3 independent experiments, with 50 random T cells analyzed per experiment. (C) T cells from CLL patients or age-matched healthy donors were allowed to conjugate with autologous CLL cells or healthy B cells, respectively, with or without sAg (blue, CMAC dyed). Conjugates were then fixed and stained with rhodamine phalloidin to detect F-actin (red). Note the lack of F-actin enrichment at the synapse site in T cells from CLL even in the presence of sAg-pulsed CLL cells. Original magnification, ×63. (D) Conjugates were selected at random for imaging and were scored for accumulation of F-actin at the immune synapse. Each data set shows the mean ± SD from 9 independent patient experiments, with 50 conjugates analyzed per experiment.