Fig. 2.
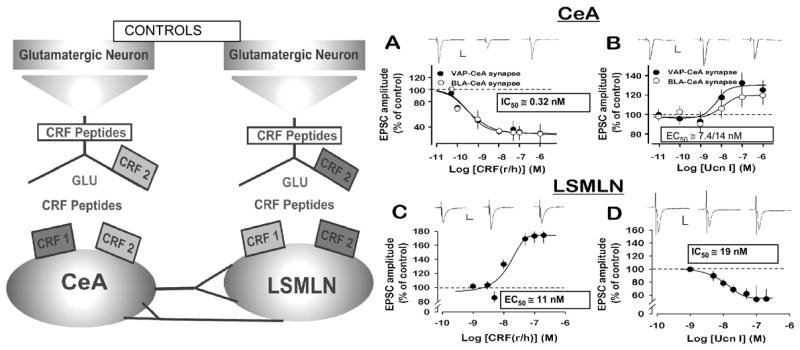
Distribution and regulatory functions depicted for CRH1 and CRH2 synaptic receptors upon excitatory synaptic transmission, [facilitatory-light gray and depressant-dark grey]. CRH1 and CRH2 receptors regulate glutamatergic transmission within synapses in the central amygdala nucleus, Left, and lateral septum medial lateral nucleus, Right. R\hCRF and Ucn I (Urocortin I), CRH1 and CRH2 receptor agonists, respectively –each produce opposite effects to inhibit or facilitate excitatory transmission-monitored as excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs)-in the two different limbic nuclei, central amygdala nucleus and lateral septum mediolateral nucleus. Note low nanomolar effective concentrations. Adapted From: J. Neurosci.,24, 4020–4029.
